[
] 149
W
ater
E
ducation
and
I
nstitutional
D
evelopment
Reservoirs were finally developed, based on the analysis
and findings in the conceptual framework plan and six
component plans.
This strategic plan, which incorporates the Integrated
Lake BasinManagement (ILBM) principles, was completed
in 2009 and set the direction for future concerted action
by all stakeholders to sustainably manage the inland water
resources in the country. The national strategic plan was
tabled to the National Water Resources Council in 2012,
where the strategies were deliberated and endorsed for
implementation. Among the national strategies advocated
in the national strategic plan is the setting up of a steer-
ing committee at federal level and a lake management
committee at the state level, to oversee the implementa-
tion of lake management based on an integrated lake basin
approach throughout the country. As with other countries
that comprise federated nations, fragmented authority and
conflicting mandates are common challenges in Malaysia.
The national lake and reservoir management committee
will become a platform to improve coordination and coop-
eration between different ministries, federal agencies and
water-related institutions. The committee will also look
into the provision of legislation, sufficient financing and
political commitment through the development of poli-
cies on lakes. At the state level, local coordination is being
strengthened through a central state committee that will
address lake issues at the catchment scale by engaging
with stakeholders and communities on matters related to
land and water in its jurisdiction. A detailed plan of action
for managing lakes and reservoirs is also being prepared to
provide a road map for implementing ILBM for the health
of the country’s inland water resources.
pertaining to lakes and reservoirs in the country. This national collo-
quium was the first step towards dealing with the issues causing the
degradation of these important inland water resources, providing
a platform for meaningful discussion as well as knowledge-shar-
ing among the various participants. Subsequently, the colloquium
provided the initial inputs, and enabled further collaboration for
consequent action, towards the formulation of a national framework
and consolidated plan for sound lake management in Malaysia.
A Technical Committee on Lake Management was later jointly estab-
lished by ASM and NAHRIM to move the national agenda forward and
articulate strategies to support the sustainable management of lakes
and reservoirs in Malaysia. A framework for action was undertaken
in 2008 to establish a comprehensive plan using a multi-stakeholder
consultative planning approach, beginning with a preliminary concep-
tual framework plan. The first multi-sector workshop involving
stakeholders from government agencies, the public and private sectors
and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) was held at NAHRIM
in January 2008 to institute the Conceptual Framework for Lakes and
Reservoirs Management. The ‘logical framework approach’ was used as
a planning instrument to guide stakeholders in the workshop in their
analysis of the prevailing situation and any proposed measures to be
undertaken. The final conceptual framework Plan provided the input
for the draft of the vision and mission statement of the Strategic Plan.
Preparation of more detailed component plans was synthesized
from thematic position papers which were subsequently consolidated
to further refine the conceptual framework Plan. A fresh round of
stakeholder consultations was held for each of the six themes: govern-
ance, management, research and development, capacity building,
information management and community stakeholder participation.
These consultations helped to refine the earlier findings and formu-
late plans of action for each component. The final National Strategic
Plan for the Sustainable Development and Management of Lakes and
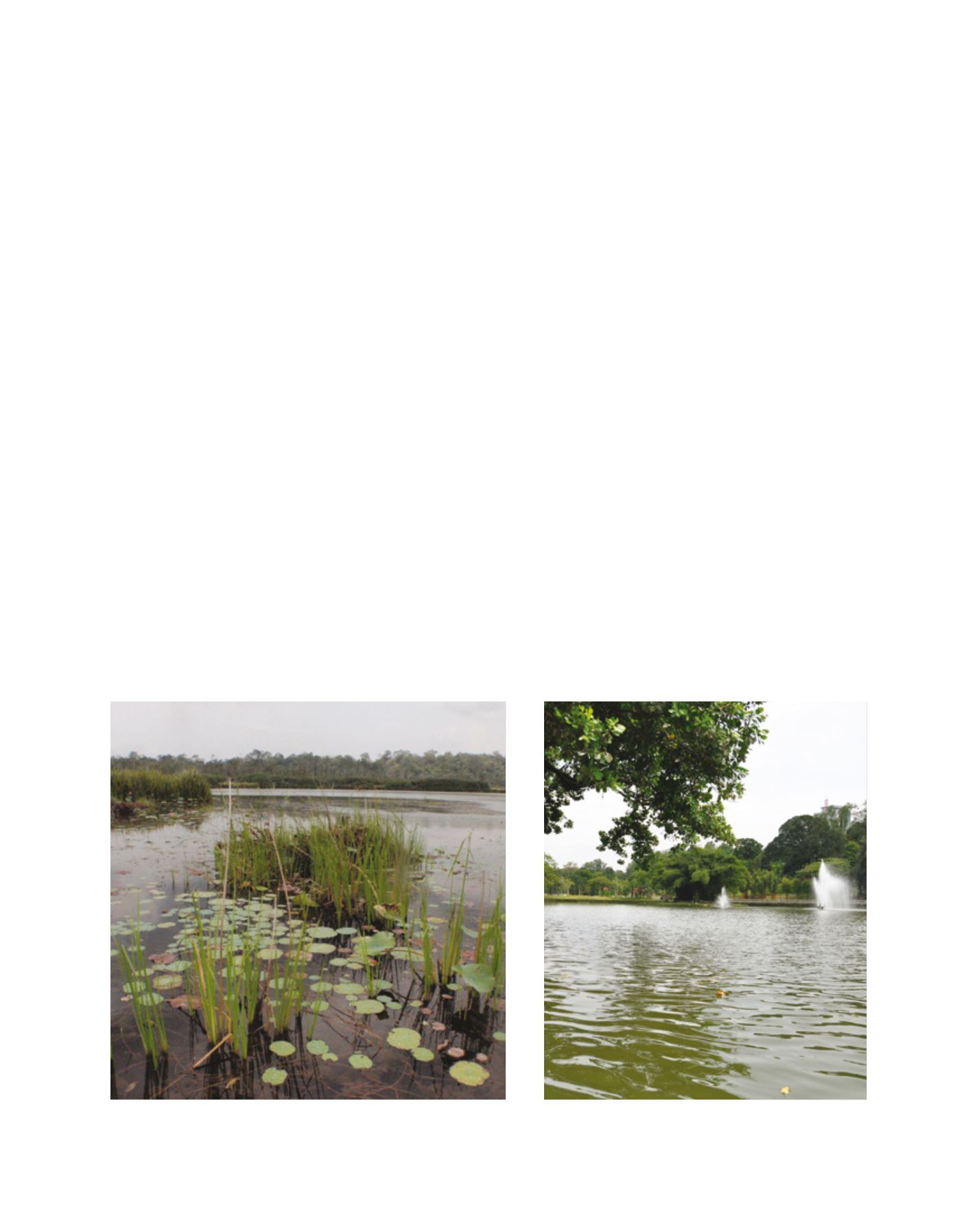
Chini Lake, the second largest freshwater natural lake in Malaysia. The lake shores
are inhabited by the aborigine Jakun tribe
Image: NAHRIM
Perdana Lake in Perdana Botanical Gardens, the oldest and most
popular park in Kuala Lumpur
Image: NAHRIM