[
] 110
G
overnance
and
P
olicy
major focuses of ITU’s work. For instance, in the last few years ITU
Recommendations have approved standards for the development of
next-generation networks
4
that will reduce energy consumption by 40
per cent compared to the present public switched telephone network.
Another recommendation, to switch from analogue to digital broad-
casting, may reduce the energy consumption of powerful broadcasting
transmitters by 10 times. As there are hundreds of thousands of
broadcasting transmitters, some with power up to 100-150 kilowatts,
the GHG emission reduction could be very significant.
ICTs can play a vital role in the reduction of GHG emissions in
other industries. Forecasts estimate that they could help cut emis-
sions by 15 to 40 per cent, by reducing or substituting business
travel by audio- and video-conferencing and remote collaboration,
providing means for remote working, enabling intelligent transport
systems, improving supply chain management and using ‘smart’
building technologies.
ITU develops international standards, guidelines and other docu-
ments facilitating the introduction of environment-friendly ICT
equipment and networks in telecommunications and other industries.
Businesses around the world could unlock global energy efficiency
savings of over EUR500 billion by systematically using ICTs.
ICTs and adaptation to climate change
According to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate
Change: “Adapting to climate change entails taking the right meas-
ures to reduce the negative effects of climate change (or exploit the
positive ones) by making appropriate adjustments and changes.”
There are many measures that are necessary to respond to climate
change. One is the establishment of an environment observa-
tion system that predicts, identifies and measures the extent of the
problem, while also providing data for the development of effective
response strategies. This needs to be combined with an
early warning and emergency telecommunication system,
which takes information obtained by the observation
system and uses it for the generation and distribution of
warning signals and for planning relief operations.
ICTs are the main components of both systems.
Wireless communications were used for the first time in
saving the lives of hundreds of sailors aboard the battle-
ship General-Admiral Apraksin at the end of the 19th
century. Since that time the importance of emergency
telecommunications has increased significantly. Early
warning and emergency telecommunications, both
wired and wireless, have saved hundreds of thousands
of lives during recent decades.
The development of regulations and standards for early
warning and emergency telecommunication systems has
been one of the key activities of ITU since its inception.
Standards such as recommendations on signaling protocols
and Common Alerting Protocol on the use of radiocom-
munications serve as the technical basis for these systems.
International spectrum management functions,
fulfilled by the ITU secretariat, assist in the develop-
ment and effective operation of space and terrestrial
radiocommunication networks. These are particu-
larly important in disaster relief activities when wired
communications are damaged or completely destroyed.
ITU and climate change
The use of ICTs for combating climate change is
among the most important items on the agenda of ITU
conferences and assemblies. ITU has adopted several
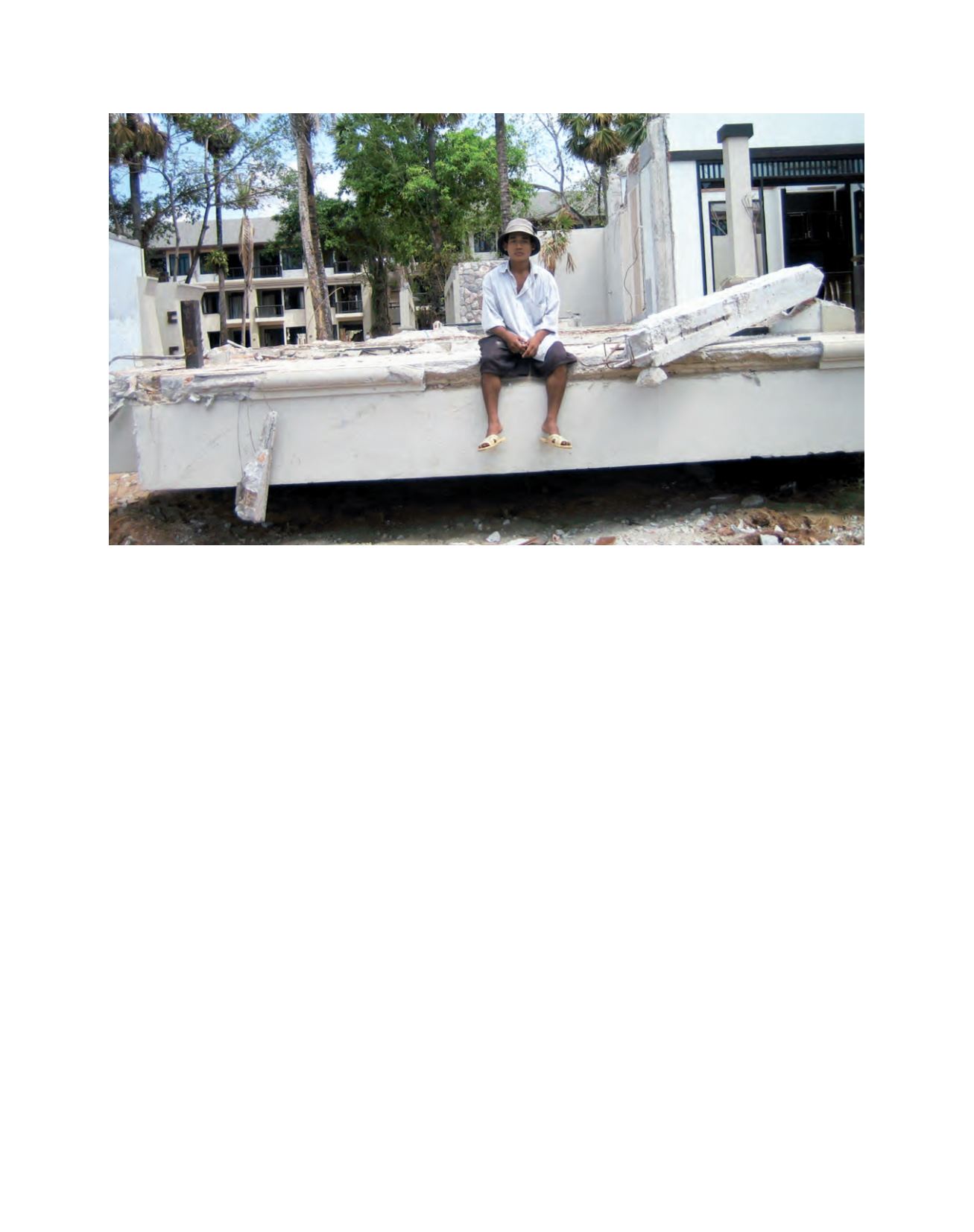
Destroyed building in Banda Aceh, Indonesia
Image: ITU/C. Zavazava