
[
] 253
lines the need for greater collaboration to conserve
the region’s globally significant biodiversity. As
Secretariat, ACB supports the programme by promot-
ing the parks, developing resource materials and
enhancing the capacity of PA managers.
Invasive alien species management
Invasive alien species (IAS) are plants, animals or micro-
organisms that have been introduced outside their natural
distribution area and exhibit sufficiently rapid growth,
reproduction and dispersal to become highly competitive
and destructive to native species, particularly if the new
ecosystem lacks the predators or pathogens of their own
native range. The cost of damage caused by IAS globally
is estimated at US$1.4 trillion per annum. In the ASEAN
region, these species are becoming a threat to biodiversity
and the economy. They are a major driver of environ-
mental change, constraining environmental conservation,
economic growth and sustainable development.
With financial assistance from the European Union,
ACB implemented the Joint Research/Initiatives (JRI)
on Biodiversity Programme from 2008-2010. Through
the JRI, ACB provided technical and financial aid in the
access and benefits sharing. It advocates a holistic approach to biodi-
versity conservation that emphasizes the importance of synergy in the
natural environment.
Following its multi-sectoral paradigm, ACB has fostered forest
biodiversity through several initiatives.
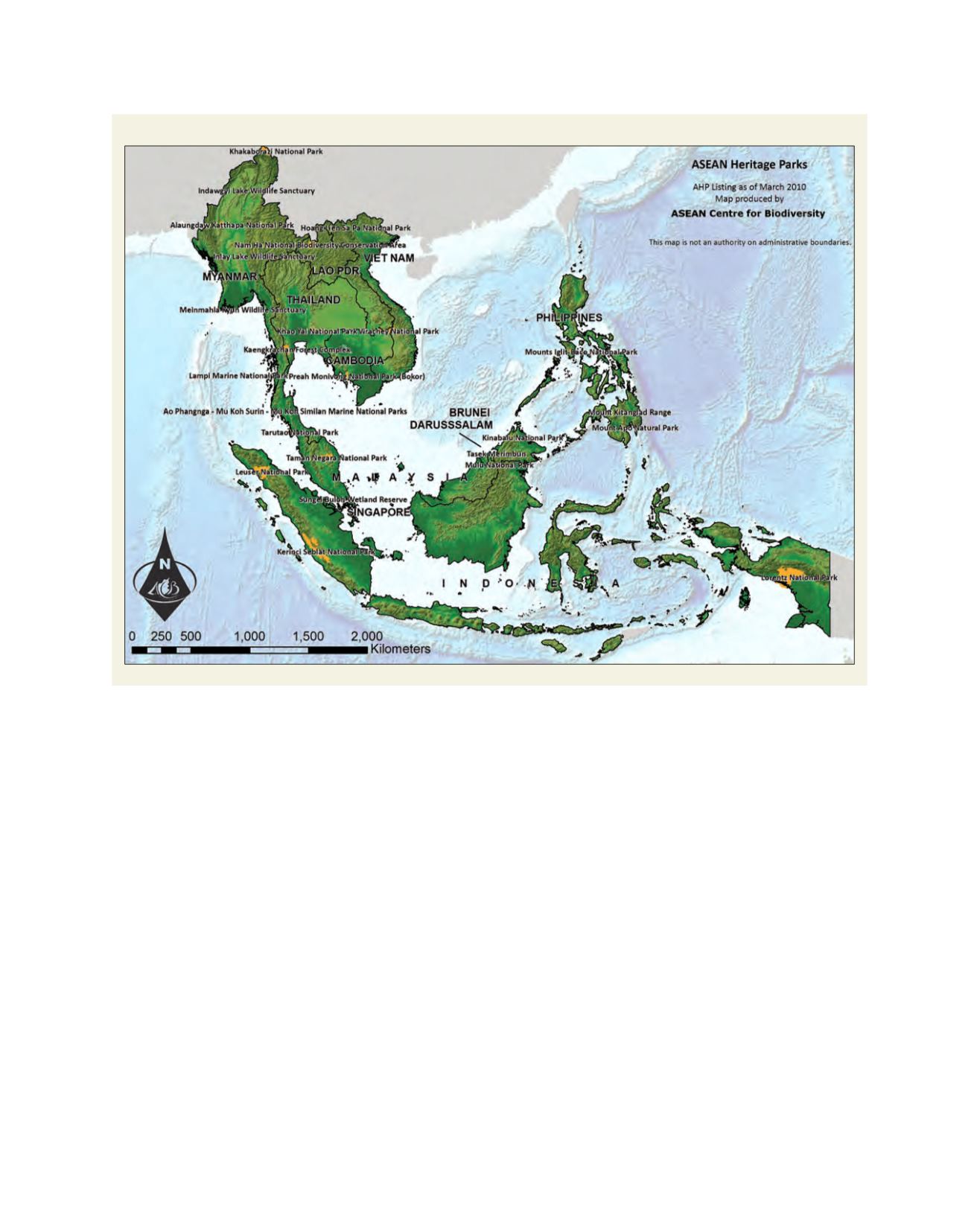
ASEAN Heritage Parks
The establishment of protected areas (PAs) remains one of the key
cornerstones of biodiversity conservation. The Philippines, Indonesia
andMalaysia have the highest number of PAs while Indonesia, Thailand
and the Philippines have the most expansive areas. The region has also
exceeded the suggested target of declaring ten per cent of its terrestrial
land PAs, having established 13.2 per cent for such purpose. Six ASEAN
Member States have exceeded the 10 per cent target and of these, Brunei
Darussalam, Cambodia and Thailand have set aside more than one fifth
of their total land area for protection and conservation.
Protected areas are established as ASEAN Heritage Parks (AHPs)
to generate greater awareness, pride, appreciation, enjoyment and
conservation of the region’s rich natural heritage. AHPs are defined as
‘PAs of high conservation importance, preserving in total a complete
spectrum of representative ecosystems of the ASEAN region’.
4
The ASEAN Declaration on Heritage Parks was signed in
December 2003. The corresponding AHP Programme under-
ASEAN Heritage Parks
Source: ASEAN Centre for Biodiversity
















