
[
] 52
Strengthening national forest programmes
Ewald Rametsteiner, Food and Agriculture Organization
and Jerker Thunberg, National Forest Programme Facility
M
ore than a decade ago, countries recognized the
importance of comprehensive forest policy frame-
works. They agreed on a common approach known as
national forest programmes (NFPs) to achieve sustainable forest
management. Acknowledging the validity of diverse approaches
to implementing sustainable forest management (SFM), coun-
tries also adopted a set of principles designed to guide NFP
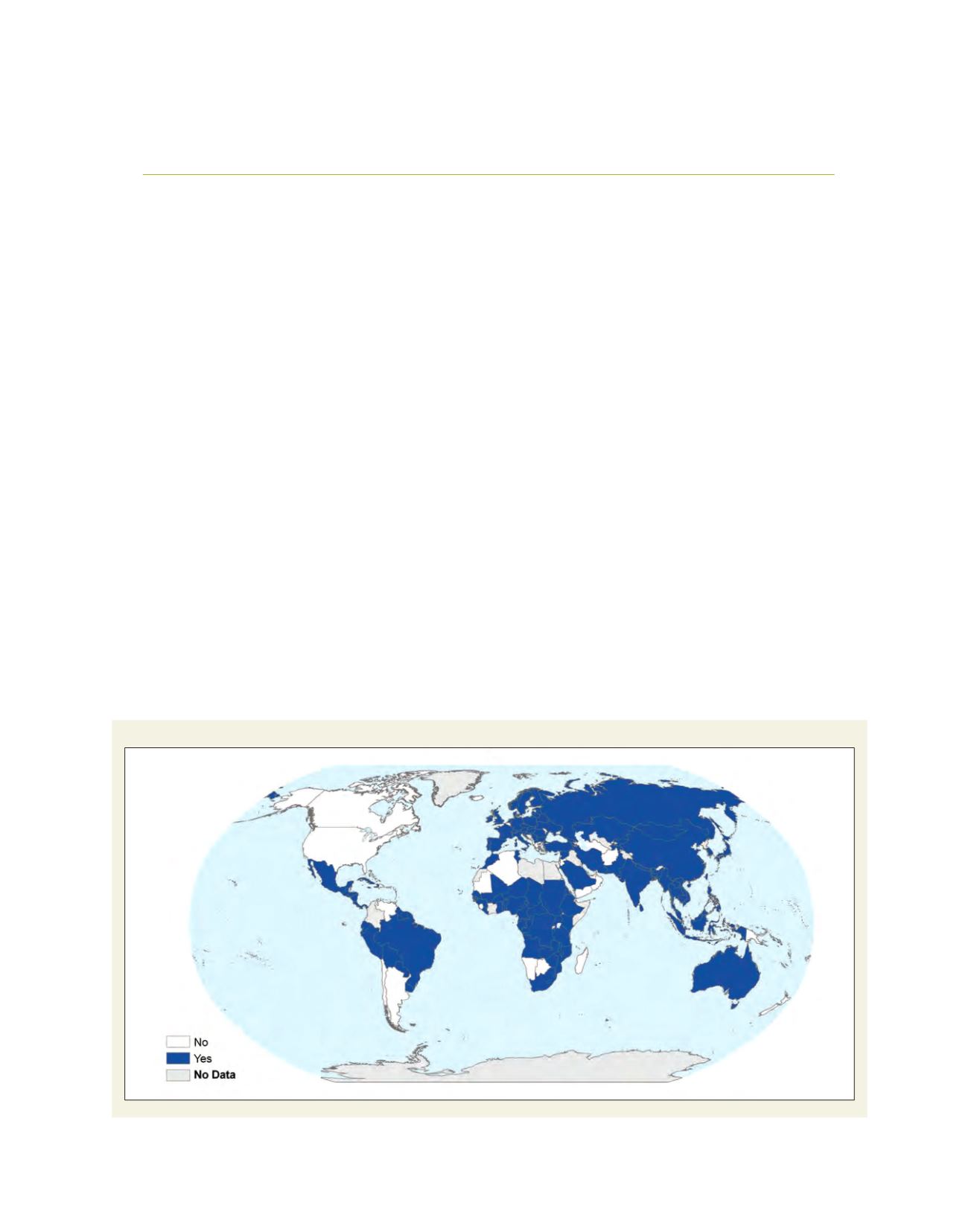
development and implementation. Today, NFP processes are
under way in more than 130 countries, according to the Food
and Agriculture Organization (FAO) Global Forest Resource
Assessment 2010.
The NFP Facility, hosted by FAO, was created in 2002 as a
mechanism to assist countries in developing and implementing
NFPs that address local needs and national priorities effectively
and reflect internationally agreed principles. Aiming to play a
catalytic role, the NFP Facility stimulates broad stakeholder
participation in the NFP process by providing grants directly
to civil society to implement planned NFP activities. The NFP
Facility also facilitates capacity-building and information serv-
ices. By 2011, it supported 70 countries and four regional
initiatives, involving more than 800 local organizations in forest
policy formulation and implementation activities.
Many other international organizations, donors and
development partners have provided assistance for
NFP processes in various countries.
Since the mid-1990s, many countries have made
substantial progress in implementing NFPs and its prin-
ciples. The following are some of the major experiences
gained by the NFP Facility and FAO in support-
ing NFPs. These provide valuable lessons on how to
improve future implementation of NFPs.
A comprehensive governance framework for forest-
related activities
Emerging issues such as climate change, forest law
enforcement and the green economy have had a direct
effect on forests and the way they are managed and
used. In many countries, there has been a prolifera-
tion of forest-related initiatives, including on reducing
deforestation and forest degradation (REDD) or forest
law enforcement and governance (FLEG). This has
increased the need for greater consistency and coordi-
nation among initiatives. The wide adoption of NFPs
Countries reporting the existence of a National Forest Programme
Source: FAO Global Forest Resource Assessment 2010
















