
[
] 93
Two decades of forest
investment best practice
Ian Gray, Ulrich Apel, Linda S. Heath, Jean Marc Sinnassamy, SFM/REDD+ Team and
Gustavo A. B. da Fonseca, Team Leader, Natural Resources, the Global Environment Facility
F
or 20 years, the Global Environment Facility (GEF) has
recognized the importance of forests for their role in
sustaining biodiversity, their ability to provide a range of
important environmental services and their potential to contrib-
ute to many countries’ sustainable development plans.
The GEF has become an important supporter of developing coun-
tries’ efforts to manage their forests sustainably. Since its inception in
1991, it has financed over 330 projects and programmes focusing on
forest conservation and management in nearly 100 developing coun-
tries. The total GEF allocation to forest initiatives during this period
amounts to more than US$1.5 billion, leveraging US$6.8 billion from
other sources. Through the years GEF support has encompassed a
mix of traditional forest management approaches such as protected
areas and integrated watershed management, while also piloting new
and emerging aspects such as the role of forests in climate change
mitigation. GEF’s forest approach now reflects a diverse portfolio of
projects that either address individual GEF focal area
aspects of forests or emphasize the multiple benefits of
forest ecosystems. All types of forests, ranging from tropi-
cal and subtropical forests to woodlands and trees in the
wider landscape, are covered by these projects. The port-
folio also presents a wide spectrum of sustainable forest
management (SFM)
1
tools that are promoted through
GEF projects such as protected area management,
certification of timber and non-timber forest products,
community-based forest management and payments for
ecosystem services (PES).
GEF projects have financed projects addressing the
seven SFM thematic elements as defined by the United
Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF) and used by the
Food and Agriculture Organization in its Global Forest
Resource Assessment (2010).
In the current replenishment cycle GEF-5 (FY 2011-
2014), the GEF is expanding and strengthening its SFM
efforts, including in the field of climate change miti-
gation, to harness the opportunities for forests in the
international Reducing Emissions from Deforestation
and Forest Degradation in Developing Countries
(REDD+) agenda. The GEF’s SFM/REDD+ strategy seeks
to create multiple global environmental benefits from the
management of all types of forests and the strengthen-
ing of sustainable livelihoods for people dependent on
forest resources, in all 143 eligible countries. The GEF
has established an incentive mechanism to encourage
countries to invest significant fractions of their System
for Transparent Allocation of Resources (STAR) funding
allocations from biodiversity, climate change and land
degradation focal areas into more comprehensive SFM/
REDD+ projects and programmes. The STAR system
determines the amount of resources that a given country
can access from the GEF during the current cycle.
The allocation of resources to SFM/REDD+ projects
and programmes draws on a transparent and equitable
investment formula that provides an incentive in a ratio
of 3:1. In other words, for every three dollars of invest-
ment from countries’ STAR allocations, one dollar will
be released from the SFM/REDD+ incentive mechanism
to the project or programme proposed. In this way, the
GEF expects a total investment of up to $1 billion into
SFM/REDD+ during the current replenishment phase.
The SFM/REDD+ strategy is fully responsive to the
guidance provided by the United Nations Framework
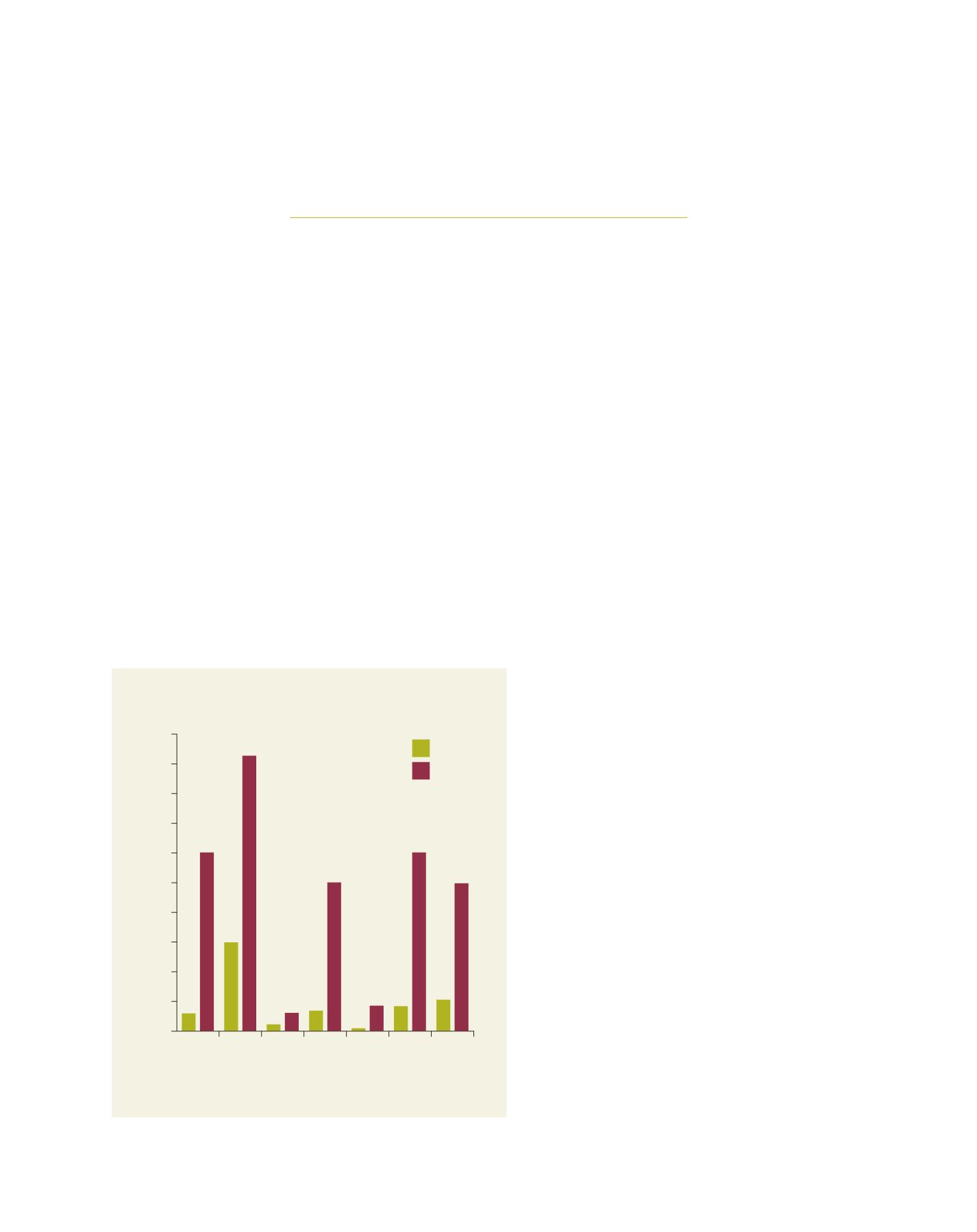
Extent of
forest resouces
US$ Millions
0
Biological
diversity
Health
and vitality
Productive
function
Protective
function
Socio-econimic
function
Enabling
framework
200
400
600
800
1,000
1,200
1,400
1,600
1,800
2,000
GEF funding
Co-finance
GEF funding to forest projects 1991-2011 by the
seven SFM thematic elements
Source: GEF
















