[
] 100
Capacity development for water cooperation
Dr Reza Ardakanian and Lis Mullin Bernhardt, UN-Water Decade Programme on Capacity Development
T
he year 2013 is of particular significance to UN-Water,
the United Nations coordination mechanism for water-
related issues: not only does it mark the 10-year
anniversary of UN-Water’s founding, but it is also, through the
International Year of Water Cooperation (IYWC 2013), serving
to cast a spotlight on the importance of cooperation in water-
related sectors. Indeed, this desire for cooperation on water
issues was a key reason for the formation of UN-Water, which
was created in order to foster greater collaboration and infor-
mation sharing among existing United Nations agency members
and external partners.
1
The need for strengthened collaboration and coherence among
the United Nations entities dealing with freshwater and sanitation
issues is as great today as it was when UN-Water was founded. As
UN-Water’s capacity development office, the UN-Water Decade
Programme on Capacity Development (UNW-DPC)
2
fosters
cooperation in capacity development activities in a
broader sense that has impact beyond the boundaries
of UN-Water.
The case for capacity development in
water cooperation
Capacity development and cooperation are funda-
mentally linked and mutually dependent. It is no
coincidence that one of the five major objectives of
IYWC 2013 relates to it, explicitly calling for the
need to “enhance knowledge and develop capacity
for water cooperation”.
3
Water cooperation can take on different forms of
meaning, design and application depending on the
nature, aspect and context of cooperation. It has politi-
cal, educational, scientific, cultural, ethical, social,
religious, legal, institutional and economic facets.
W
ater
E
ducation
and
I
nstitutional
D
evelopment
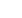
Used safely, wastewater can help to alleviate the increasing pressure on freshwater resources, particularly in urban and peri-urban areas
Image: UN-Habitat