and development. Water-related issues are inextricably
intertwined with economic, social and environmental
issues, and as global issues (for example in the form
of water disasters stemming from climate change),
they require the close cooperation of all the relevant
players, including governments, international institu-
tions, non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and
the public and private sectors, if they are to be solved
or managed. The key role of effective water resources
management in Korea’s development can provide
a good example to developing countries seeking
ways to develop and manage their water resources.
Moreover, at the core of this effective water manage-
ment has been K-water, which from its founding has
been working in cooperation with related organiza-
tions and NGOs. This cooperation has not only been
in the area of water resources management, but also in
the area of cooperation with countries concerned with
economic development.
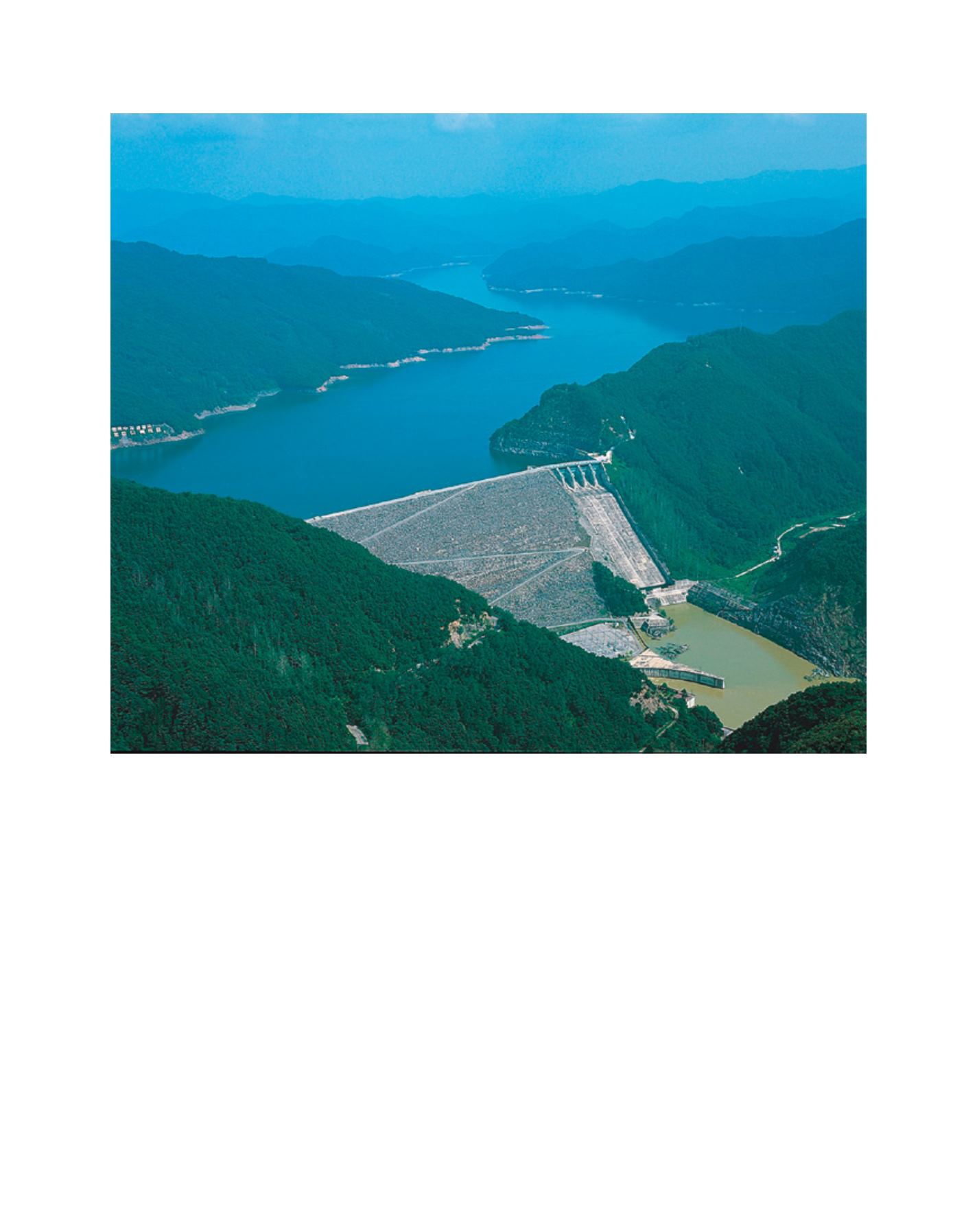
Soyanggang Dam case is that it employed a domestic company
to undertake the large-scale project, thereby promoting indus-
trialization and strengthening the government-business ties that
became the hallmark of Korea’s development.
More recently, since 2006, the Government through the Ministry
of Environment has enabled investments from the private sector into
the sewerage business. The objective of this measure is to increase the
competitiveness of the sewerage business through the incorporation
of private sector funds and technology. Through this public-private
partnership, investments of KRW 243.8 billion won (US$220 million)
have been made in the sewerage of Gimpo City,
18
and plans are in place
to invest KRW 172.3 billion (US$150 million) in Gunja City’s sewer-
age.
19
According to 2011 figures, among the 496 sewage disposal plants
that handle over 500 tons of waste daily, 70 per cent operate through
consigned management while the remaining 30 per cent are directly
operated by local governments. Among these, 17 per cent, or 85 loca-
tions, are build-transfer-operate projects.
20
As Korea’s development experience shows, effective, cooperative
water resources management has been an essential part of growth
The Soyanggang Dam exemplifies the government-business cooperation at the heart of Korea’s development
Image: K-water
270
E
conomic
D
evelopment
and
W
ater