[
] 261
Climate-related services in China
Huijun Wang and Dabang Jiang, Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
C
hina is situated in East Asia, bordered on its east by the
western North Pacific. The national climate is modu-
lated mainly by the East Asian monsoon circulation,
the western North Pacific subtropical high, surface conditions
on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, the South Asian high pressure
system in the upper troposphere, atmospheric circulation in
the middle and high latitudes of the Eurasian continent, and
remote factors through atmospheric teleconnection. Spatial
and temporal climate conditions are quite complicated in
the country, with warm-wet climates in summer and cold-
dry climates in winter. The national natural environment,
highly influenced by geographic location and topographic and
geomorphic features, is generally poor, and most regions are
susceptible and vulnerable to climate change. A considerable
effort has been made by meteorologists and climatologists to
investigate the facts and mechanisms of climate change over a
wide range of timescales and to evaluate its influence. At the
moment, climate service products generally consist
of climate detection and diagnosis, climate predic-
tion and projection, climate resource development,
climate risk management and so on. Climate serv-
ices are provided for agriculture, hydrology, traffic,
disease prevention and atmospheric environment
control among other uses.
Climate change-related services
Meteorological stations have increased in China since
the 1950s. The network of automatic meteorologi-
cal stations currently includes more than 2,000 sites
across the country. In addition, there are satellite
data and marine observations as well as observation
stations for wind and solar energy. Based on these
continuous and quality-controlled observations, it
has been found that China’s climate has undergone
C
apacity
D
evelopment
75E 85E 95E 105E 115E 125E 135E
20N
30N
40N
50N
> 0.4
> 0.2
> 0
< 0
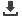
Spatial distribution of linear trends of annual mean temperature with 160 stations in China from 1951-2010. Units:
o
C/decade
Source: IAP China