
[
] 128
such as bush encroachment, a major rangeland problem in
south-west Africa (see case study).
Partnering with international financing institutions for
sustainable land practices in developing countries
Since 2008, ESA has taken important steps to showcase the
potential of satellite observations to support sustainable devel-
opment initiatives in developing countries by international
financing institutions (IFIs) and multilateral development
banks such as the World Bank, the United Nations International
Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) and recently the
Asian Development Bank and the Global Environment Facility.
EOmethods have proven to be important tools for the sustaina-
ble management of lands in water-scarce environments: assessing
land productivity, detecting decreased productivity due to diseases
or reduction of water; mapping crop areas and types, estimating
the conversion of natural resources into agricultural lands and
assessing impact such as degradation of ecosystems; collecting
statistics on crop production, providing yield estimations using
agrometeorological modelling; estimating land suitability for
optimum land use, reducing risks such as soil erosion; helping
management of water resources, monitoring availability of surface
waters and estimating water needs and use for irrigated crops;
supporting climate resilience and adaptation strategies and assess-
ing impact of climate change on natural resources.
A joint ESA-IFAD project developed a Land Erosion Risk
indicator in Niger, which together with information on land
use changes allowed the assessment of agricultural practices,
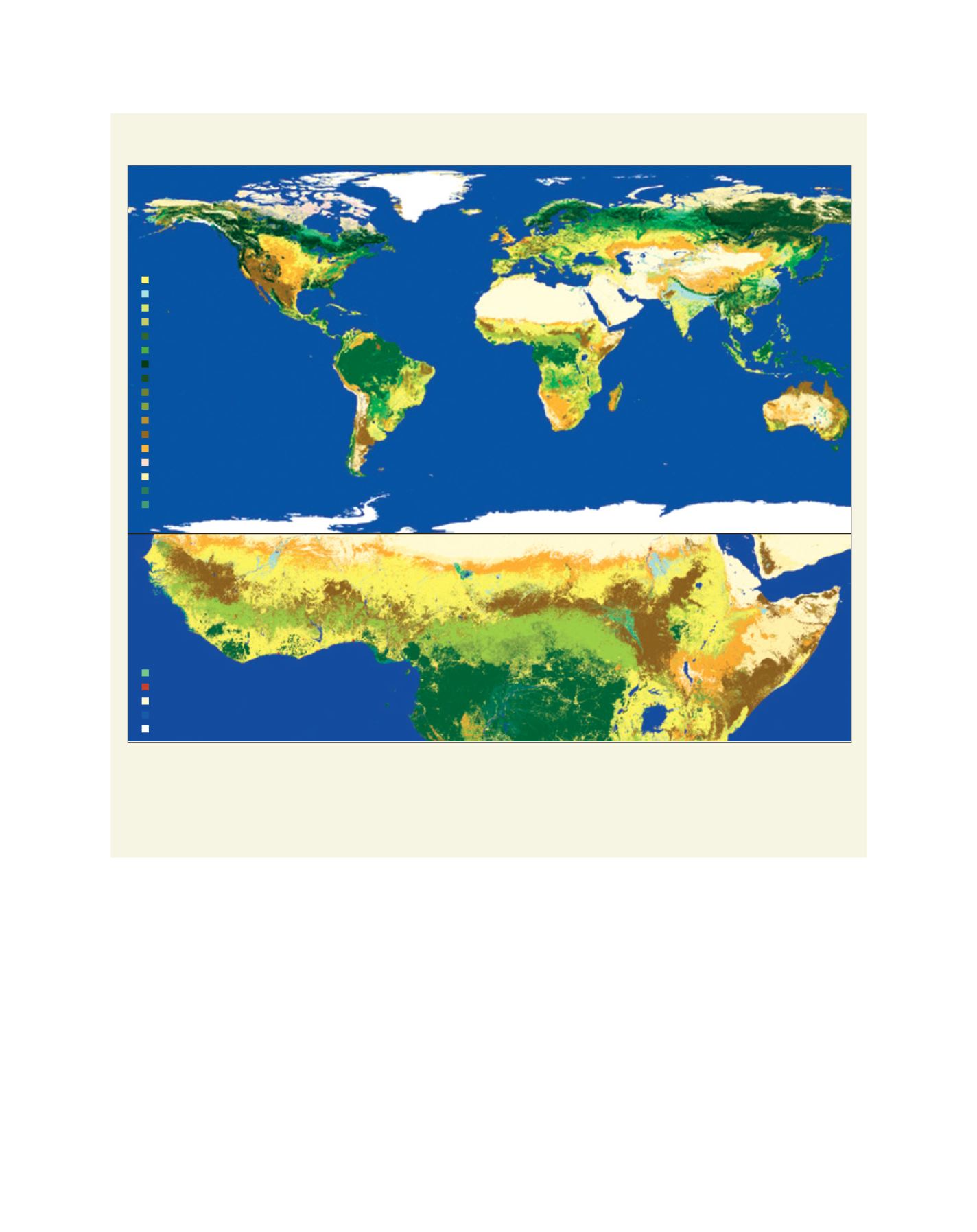
Case study: Global land cover mapping
The ESA CCI has produced a three-epoch series of global land cover maps at 300 m resolution (2000, 2005 and 2010). The land cover maps follow a
legend based on the United Nations Land Cover Classification System with 22 high-level classes for global use and 14 subclasses for regional adaptation.
Source: ESA CCI Land Cover project/Université Catholique de Louvain
The 2010 Global Land Cover map
Mosaic cropland/vegetation
Mosaic vegetation/cropland
Tree needleleaved evergreen
Cropland irrigated/post-flooding
Cropland, rainfed
Tree needleleaved deciduous
Tree mixed leaf type
Tree broadleaved deciduous
Tree broadleaved evergreen
Mosaic tree, Shrub/HC
Mosaic HC/tree, shrub
Grassland
Lichens and mosses
Shrubland
Sparse vegetation
Tree flooded, fresh water
Tree flooded, saline water
Shrub or herbacaous flooded
Bare areas
Water bodies
Permanent snow and ice
Urban areas
Mosaic cropland/v getation
Mosaic
/cropland
Tree needl le ved evergre n
C opland irrigated/post-flooding
Cropland, rainfed
Tree eedleleaved deciduous
Tre mixed leaf type
br adleaved deciduous
br adleav d evergreen
Mosaic tre , Shrub/HC
Mosaic HC/tree, shrub
Grassland
Lichens and mosses
Shrubland
Sparse vegetation
Tree flooded, fresh water
Tree flooded, saline water
Shrub or herbacaous flooded
Bare areas
Water bodies
Permanent snow and ice
Urban areas
L
iving
L
and
















