Other health-related uses for integrated Earth observations will
include: forecasting potential famines; evaluating the quality and
quantity of water and soil needed or available for human use; antic-
ipating water-borne diseases, harmful algal blooms and seafood
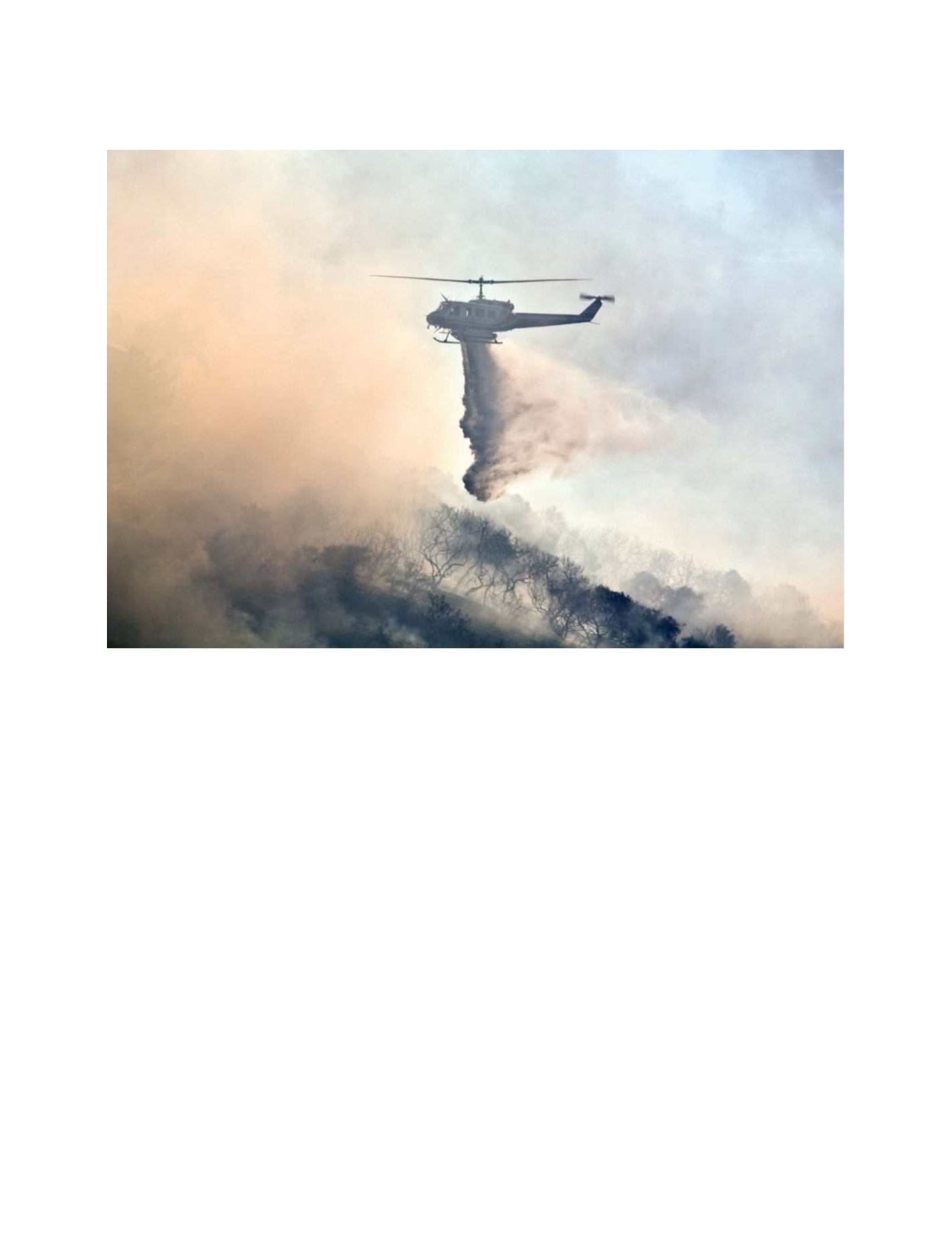
contamination; addressing the risks of wildland fires, severe weather
events and pollution. The key is presenting such comprehensive
data sets to health service providers, researchers, policy makers and
the general public in user friendly formats that make rapid action
possible.
Energy
Improving the management of energy resources, a trillion-dollar
economic sector that includes coal, oil and gas as well as solar, wind
and hydropower resources, is of critical importance to all countries.
Key issues include reliable access to energy, the efficient manage-
ment of energy resources, stabilizing or reducing greenhouse gas
emissions, and reporting energy emissions levels to the UN Climate
Change Convention and other bodies.
GEOSS will help governments and companies to manage the envi-
ronmental impacts of energy, match energy supply and demand,
reduce weather-related and other risks to energy infrastructure,
provide more accurate inventories of greenhouse gases and pollu-
tants, and evaluate the potential of renewable energy sources.
More specifically, GEOSS will provide data and information rele-
vant to: monitoring and forecasting fluctuations in hydropower, solar,
ocean and wind energy sources; assessing and predicting the envi-
ronmental impacts of energy-resource exploration,
extraction, transportation and exploitation; and to
informing energy-policy planning in both developing
and developed countries.
Activities to strengthen the contribution of GEOSS to
energy management are being carried out by the Energy
Community of Practice, an international network of
GEO members and participating organizations. The
Community’s current activities include providing online
information and other resources, enhancing the inter-
action between various energy interests and between
developed and developing nations, promoting training
and education, integrating Earth observation data more
firmly into the policymaking process, and engaging a
wider array of stakeholders and professional societies in
related fields such as sustainable buildings and carbon
capture and storage.
Climate
Understanding, assessing, predicting, mitigating and
adapting to climate variability and change will produce
important benefits for every person on the planet.
Virtually every economic sector, social activity and
ecological system is affected by long-term climate
change, natural climate variability, and extreme weather
and climate events.
[
] 153
S
OCIETAL
B
ENEFIT
A
REAS
Disaster risk reduction and mitigation provisions and a multi-hazard/multi-risk approach are key to development planning