[
] 199
Adaptation to climate change in the
mountain forest ecosystems of Armenia
Anahit Hovsepyan, Head of Climate Research Division, Armenian State Hydrometeorological and Monitoring Service;
Levon Vardanyan, Director, Armenian State Hydrometeorological and Monitoring Service;
Aram Ter-Zakaryan, Task Leader, Adaptation to Climate Change Impacts in Mountain Forest Ecosystems of Armenia,
UNDP & GEF-SPA Project, UNDP Armenia
A
rmenia’s forests are unevenly distributed across the country.
The area of forest lands in the Syunik region in the south-
east of the country extends to 94,243 hectares, including a
forest-covered area of approximately 65,000 hectares (20 per cent of
the country’s forests). In contrast, cropland totals 27,345 hectares.
The high level of biodiversity is one of the most important features
of the Syunik region. Various types of ecosystems are represented
here, including semi-deserts, arid open forests, oak forests, steppes
and tragacanth formations as well as aquatic and marsh growth,
alpine and sub-alpine vegetation, and petrophilous vegetation.
Based on assessments of the impacts of climate change, including
variability, the Syunik region has been identified as critically vulner-
able, especially in terms of the risk posed by climate change to its
unique mountain forest ecosystems
1
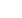
. The climate of the Syunik region
is remarkably diverse due to its complex relief and large fluctuation
of altitudes. The highest point is Mount Kaputdzhukh (3,906m
above sea level) and the lowest is the depression in the Megrin gorge
(375m above sea level). The high altitude, orientations of the moun-
tain ranges and occluded borders of the river valleys and basins have
a significant impact on the region’s climate. Most of the mountain
slopes have an eastern orientation, so the air masses blowing from
the east move up the mountain slopes and cool rapidly, causing a
gradual increase in relative humidity. Vertical climate zoning is a
typical feature and air masses become significantly drier as they pass
over the mountain ranges. Air temperature fluctuates within a large
range due to altitude differences, and the spatial distribution of annual
precipitation is irregular.
Addressing climate change impacts in mountain forests
In 2008, the Government of the Republic of Armenia launched a project
funded by the Global Environment Facility (GEF) to enhance national
capacities in the forest and biodiversity sectors to adapt to the antici-
pated climate change impacts in the mountain forest ecosystems. The
implementation of the project ‘Adaptation to climate change impacts
in mountain forest ecosystems of Armenia’ is on-going and the project
will be completed in 2013.
UNDP is the implementing agency of the project and the project’s
main national counterparts are the Ministry of Agriculture and
ArmStateHydromet under the Ministry of Emergency Situations. At
the local level, the main counterparts are the Syunik Marz Department
of Agriculture and Environment Protection, Forest Enterprises and
Administrations of the Specially Protected Areas.
The main objective of the project is to assist Armenia
in enhancing the adaptive capacity of the vulnerable
mountainous forests ecosystems to climate change. One
key expected output is the development of products and
information that will assist national and local authorities
in reducing the climate change related risks and improv-
ing forest and protected area management planning and
management practices.
Institutional framework of forest areas management
in Armenia
Various forest-related laws are in place in Armenia. In
2005 the Government approved the National Forest
Policy and Strategy of the Republic of Armenia
2
and
the National Forest Programme
3
, which to some extent
address issues pertinent to climate change. In 2005, the
National Assembly also passed the new Forest Code of the
Republic of Armenia.
4
Forest governance is under the republican body
ArmForest, a State Non-Commercial Organization under
the Ministry of Agriculture. In the Syunik region, forest
E
cosystems
Source: Armenian State Hydrometeorological and Monitoring Service
Climate zones over Armenia