[
] 69
G
overnance
and
P
olicy
cumulative rainfall forecast using the multi-model
ensemble technique. Extended-range weather forecasts
and seasonal climate forecasts are also being investi-
gated for inclusion in the advisory bulletins.
Acting together, IMD and regional Meteorological
Centres add value to the above range of services by
providing a twice-weekly advisory bulletin to 130
AMFUs. This bulletin is called the Agromet Advisory
Service and provides specific advice on crops, as well
as livestock. The bulletin is usually disseminated to the
farmers through channels including the mass media and
the internet. A mechanism has also been developed to
obtain feedback from the farmers on the quality and
relevance of the forecast content, as well as the effec-
tiveness of the dissemination system.
Via the Agromet Advisory Service, the scientific
community develops different adaptation strategies
suitable for different agroclimatic regions of the country
to counter the negative effects of climate change and
extreme weather events. These adaptation strategies
include educating farmers about weather forecasts,
150 kilometres) atmosphere-only general circulation model called
HadAM3H. This model is in turn forced by the sea surface tempera-
tures generated by a coupled atmosphere-ocean General Circulation
Model called HadCM3.
PRECIS estimates a 20 per cent rise in all Indian summer monsoon
rainfall for future scenarios. Simulation for 2071-2100 indicates an
overall warming of the Indian subcontinent associated with increas-
ing greenhouse gas (GHG) concentrations. The predicted annual
mean surface air temperature rise by the end of the century is 3 to
5ºC under the A2 scenario, and 2.5 to 4ºC under the B2 scenario.
It is predicted that the warming will be more pronounced over the
northern parts of India.
10
Climate change adaptation strategies for agriculture
IMD established the Agrometeorological Advisory Service to help
Indian farmers mitigate the impacts of climate variability and
extreme weather events through agricultural planning and manage-
ment in rhythm with nature. The service provides district level
weather forecasts of up to five days for seven weather parameters:
rainfall, maximum and minimum temperature, wind speed and
direction, relative humidity and cloudiness. It also provides a weekly
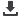
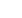
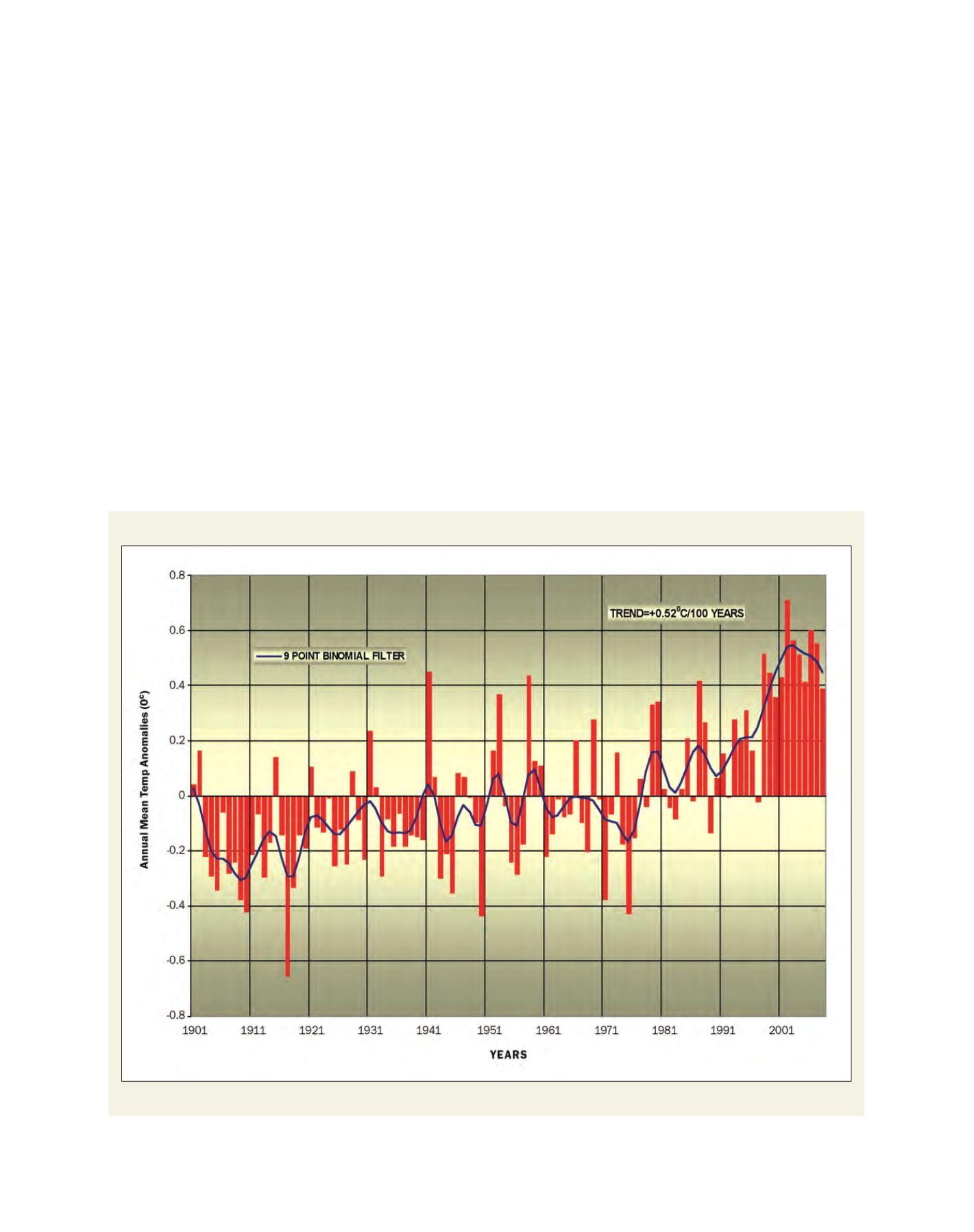
India’s annual mean temperature anomalies for the period 1901-2008 (based on 1961-1990 average)
Source: India Meteorological Department
Assessment of climate change and adaptation in India