[
] 78
G
overnance
and
P
olicy
become indispensable for many stakeholders and deci-
sion makers in the public and private sectors, where
climate risks need to be quantified and managed. The
relevant timescales range from short-term – defined
as monthly to seasonal climate fluctuations – up to
multi-decadal climate change. There is a growing
demand for integrated information on all these times-
cales, a demand which is also shaping the climate
services provided by MeteoSwiss.
Scientific research has led to a substantial improve-
ment in understanding and predicting short-term
climate variability in many regions of the world.
MeteoSwiss has started to make use of this knowl-
edge and provides both public and private clients
with probabilistic climate forecasts for the upcoming
weeks and months. Although such forecasts still have
comparatively little skill in Switzerland and Europe,
they are nevertheless valuable for a wide range of
specific applications, such as the pricing of weather
derivatives or the estimation of developments in the
energy market. To strengthen the link between fore-
cast providers and forecast users and to get deeper
insight into user demands, several joint projects have
been set up with leading international Zurich based
reinsurance companies. These projects showed that
for applications in climate risk management it is
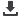
available NBCN data in order to provide high quality data series and
to address climate change and climate variability issues. Swiss NBCN
also ensures long-term continuity of measurements in the future.
Systematic long-termmeasurements also make a significant contribu-
tion to the Global Climate Observing System (GCOS) – a programme
jointly sponsored by the World Meteorological Organization, the
Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of the United Nations
Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization, the United Nations
Environment Programme and the International Council for Science.
The Swiss GCOS Office, established at MeteoSwiss in 2006, coordi-
nates all climate-relevant measurements in Switzerland. As a basis for a
legal and sustainable strategy of the national climate observing system,
GCOS Switzerland, a comprehensive inventory report was compiled in
2007.
1
Based on this report, the Swiss Federal Council decided in June
2008 to ensure the long-term continuation of at risk climate measure-
ment series and international data centres in Switzerland.
Apart from their fundamental role in climate monitoring, mete-
orological and climatological observations are relevant for many
other purposes. For example, the data are used as inputs for defining
the initial state of the atmosphere in numerical weather prediction
models, as well as being indispensable for the verification and cali-
bration of climate models.
Climate prediction and scenarios
Climate models are the backbone for providing information about
future climate in the form of climate scenarios. This information has
The Swiss National Basic Climatological Network (Swiss NBCN)
Source: Federal Office of Topography swisstopo/Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss