[
] 84
G
overnance
and
P
olicy
tion of decision makers to the problem area. The project
involved very active communication and dissemination
work. Between 2003 and 2006 more than 200 articles
were published in newspapers and journals and about
150 radio and TV interviews were broadcast on the
topic of climate change. A majority of these mentioned
VAHAVA. Among its publications and conferences are
various books, proceedings and CD-ROMs, totaling
around 4,000 pages.
To summarize, some organizational experiences that
could be useful to other countries facing similar circum-
stances include:
• In such a large and synthesizing project it is
extremely important to gain the support of leading
politicians, government officials and scientists
• Guarantees of financial support should be obtained.
In this case the leaders of the Ministry for the
Environment and Water Management and HAS
made an agreement
• The existing but underused research results of
around 300 experts were built into this synthesizing
work, secured by personal motivation and interest
• Active and constructive working relationships were
developed with the leading green non-governmental
organizations. A good relationship with the media
was established.
National climate change strategy
After the publication of the proposals, the Hungarian
Government decided on preparation of a National
Climate Change Strategy (NCCS), coordinated by
HMEW and taking into account the results and recom-
mendations of VAHAVA. Parliament unanimously
adopted NCCS on 17 March 2008. The resolution was
publications should play equally important roles. A wide range of
professionals became acquainted with new terms (‘climate policy’,
‘mitigation’, ‘adaptation’) and knowledge of the general features of
climate and weather.
Responses to impacts and their solutions can be achieved in
sequence, taking the interdependencies of mitigation and adapta-
tion into consideration. The order is: preparation; prevention of
damage; defence (rapid, professional and effective reaction, the
mobilization of reserves and disaster prevention forces); and reme-
dial action (rapid elimination of damage, especially that affecting
health and infrastructure, and the establishment of relevant insur-
ance systems, financial and other reserves). A major proposal is that
a Preventive Climate Strategy for Public Health Protection should
be developed. In a critical situation the availability of food, drink-
ing water, medicine and other reserves determines the length of an
emergency situation and how many lives are saved.
Great importance is attributed to the role of forests in reducing
damage, and of vegetation cover in general, with special regard
to their absorption and storage of CO
2
. An ever increasing stress
is the reduction of freshwater resources and deteriorating water
quality, along with rising water prices. The project intends to reduce
flooding and protect subsurface drinking water as well as thermal,
medicinal and mineral water resources.
Proposals related to the field of energy production and consump-
tion, which play a deterministic role in global warming, are
concentrated on mitigation. Strategies include improving the effi-
ciency of power generation, using energy saving technologies to
decrease power dependency and reduce costs, and expanding alter-
native power resources. A special response package was created for
transportation, aimed at reducing emissions.
Experience gained during the project
Efforts were made to involve the widest possible professional and
social groups in debating partial results. This also drew the atten-
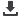
The record flooding in Budapest during August 2002. Public transport was unusable
along the riverbank, but the second dyke defended the downtown
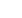
Ice drifted onto the pier by the stormy temperate latitude cyclone, Kyrill
Lake Balaton, Hungary, 19 January 2007. As well as the strong wind,
the high water level also contributed to the event
Image: VITUKI, Budapest
Image: Hungarian Meteorological Service, Budapest