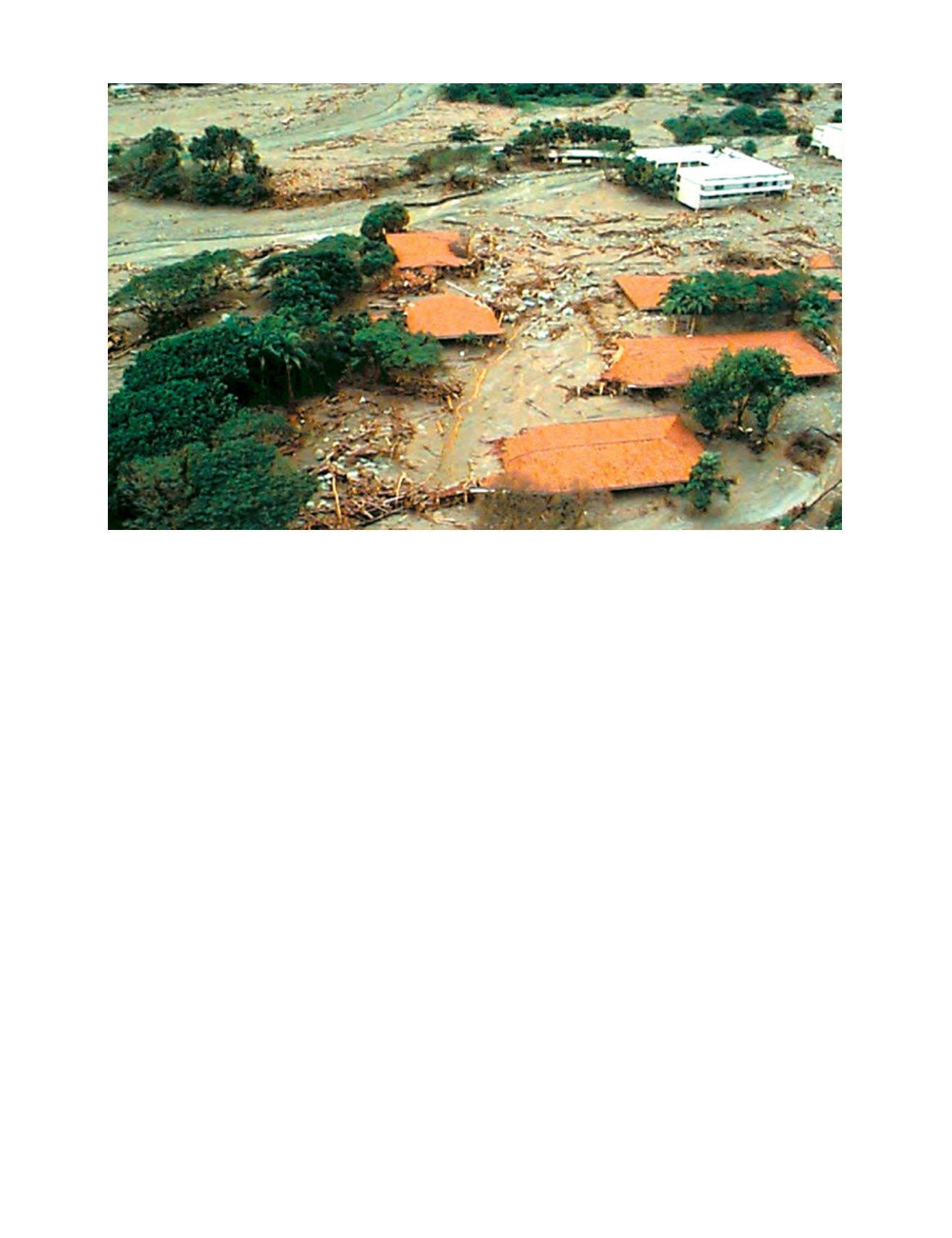
in the atmosphere and their predicted transportation and depo-
sition are essential for mitigating their disastrous impact on
populations and economies.
Increasingly accurate and reliable information on weather,
climate and water allows for improved decision-making, which
has the potential to offset the negative impacts of weather and
climate events. WMO’s authoritative information, advice and
databases are critical for natural disaster risk assessment, vulner-
ability analysis, preparedness, response and recovery. Early
warnings of weather, climate and water extremes protect life and
property, provided that they reach their target audience in a timely
and suitable manner.
Provision of weather, water and climate information, analy-
ses, forecasts and warnings to a wide range of weather-sensitive
sectors is of enormous socio-economic benefit. Agriculture,
fishery and forestry; energy and water-resources management;
land, marine and aviation transport; banking and insurance;
construction and urban design; and also human health, recre-
ational activities and tourism, all benefit directly from access to
meteorological and hydrological information. Major societal and
economic benefits for countries are expected from access to
climate information, including climate predictions and assess-
ments of climate change.
Access to meteorological, hydrological and climatological infor-
mation produced and provided by the National Meteorological
and Hydrological Services (NMHSs) is of crucial importance for
the sustainable improvement of developing and less-developed
countries in areas such as urban development and management
in the context of population pressures, water supply, pollution,
transportation and sanitation.
The collection and exchange of Earth observations (especially
related to weather, climate and water), requires the use of infor-
mation and communication technology (ICT), and is needed
for the analysis, monitoring and forecasting of the state of the
Earth. The goal is the delivery to populations of weather, climate
and water information and warnings as comprehensive and
effective services in support of the safety of life and property.
An ongoing challenge lies in the fact that developing countries,
which are among the most exposed to natural disasters and least
able to benefit from the advances in the application of weather,
climate and water information, have limited access to ICT, either
because they are unavailable or too expensive. The availability of
information technology has a key role to play in enabling and
fostering access to weather, climate and water information and
services. Information technology should help pave the way to
sustainable progress in developing and least developed countries
(LDCs), enabling populations and various economic sectors to
benefit from comprehensive effective information and warnings
which support the protection of life and property and of sustain-
able economic and social development.
ICT applications: benefits in all aspects of life
ICT applications can support sustainable development in the fields
of public administration, business, education and training, health,
employment, environment, agriculture and science within the frame-
work of national e-strategies. The Plan of Action of the Geneva Phase
of the World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) seeks to
address this issue, including actions within the following sectors:
e-Environment
Establish monitoring systems, using ICT, to forecast and monitor
the impact of natural and man-made disasters, particularly in
developing countries, LDCs and small economies.
e-Science
Promote the long-term systematic and efficient collection, dissem-
ination and preservation of essential scientific digital data, for
example, population and meteorological data in all countries.
[
] 102
Severe weather phenomena can pose serious threats