[
] 57
effectiveness; providing better and faster government services and
ensuring availability of the required information in a timely and
accurate manner. The Yesser vision is that “by the end of 2010,
everyone in the Kingdom will be able to enjoy world class govern-
ment services offered in a seamless, user friendly and secure way
by utilizing a variety of electronic means.”
Furthermore, a number of e-government projects have been
implemented or are being developed by different government
organizations. Examples include: the e-government portal, public
key infrastructure (PKI), national ID cards, e-payment gateway
(Sadad), e-tax system, social insurance system and electronic
information exchange. A number of government services are
currently available on-line, such as investment licenses, visa appli-
cations, traffic ticket enquiries and payments, passport fee
payments and utility bill payments. A yearly contest (e-Award) is
conducted to promote and recognize local initiatives, innovation
and contributions to e-services and applications.
e-Services
The Saudi Payment Network (SPAN) was one of the first coun-
trywide inter-bank retail payment networks in the world.
Implemented in 1990, SPAN is a nationwide network comprising
of thousands of ATMs and point of sale (POS) terminals. Other
e-banking systems include Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express
(SARIE) for electronic fund transfers, Tadawul (securities trading)
and Semah (a national credit bureau). Also, most Saudi banks
offer e-banking services such as phone, mobile and Internet
banking in addition to e-share trading.
The major elements for the e-Business applications are either
developed or in the final stages of development. These include:
• The legal elements. The e-transaction and e-crime acts are in the
approval phase
• The e-payment gateway “Sadad” is operational
• The public key infrastructure (PKI) is under development
• Postal services are undergoing major improvement
• Ensuring information security and privacy
Major e-business applications have been developed and imple-
mented. Examples include e-procurement systems at major
corporations such as Saudi ARAMCO and SABIC, e-umrah system
(providing religious tourism packages by linking international
travel agents, local suppliers and the related government author-
1998
1999
2000
2001
2002
2003
2004
2005
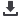
Corporatization:
Saudi Telecom
Company (STC)
• Telecom Act
• Independent
telecom Regulator
(SCC)
• PTT changed to
Ministry of ICT
• IT added to
Regulator mandate,
renamed CITC
• National ICT Plan
• Launch of smart cards
• EasyNet
• e-Gov. program “Yesser”
• Home PC Initiative
ISP Sector
Liberalization
• Telecom Bylaws
• Partial Privatization of STC
• VSAT Liberalization
• Liberalization of data and mobile
• IPO of 2nd mobile licensee (Ettihad Etisalat)
• National IT plan
• Draft e-Transaction Act
• e-Payment gateway
Figure 2: Timeline of Major ICT development and Telecom Sector Reform
ities), and an e-trade system that supports import and export
processes by linking different stakeholders like customs, ports
and agents.
The Ministry of Education is working on enhancing public educa-
tional environments by promoting curricula, preparing teachers,
developing student skills and capabilities in dealing with ICT and
building computer clubs in schools. Computer labs exist in virtually
all secondary schools and will be set up in intermediate schools as
well. Universities are increasingly adopting the e-education concept.
A Hospital Management Information System (HMIS) is currently
being implemented in over 200 hospitals and clinics across the
country. Telemedicine has been used with great success at the
King Faisal Specialized Hospital and at a cluster of military hospi-
tals. Nineteen hospitals and clinics are connected for voice and
video conferencing services as well as remote diagnostics. The
system links Saudi hospitals to medical facilities abroad for lectures
and video consultations as well as live casting of surgical opera-
tions. The Ministry of Health has also embarked on a programme
to link 25 additional hospitals in major cities and important rural
areas in an effort to further telemedicine services and infrastruc-
ture as well as provide international connectivity to these sites.
The Dammam city coast line is one of the coastal areas that enjoys advanced
mobile telecommunications service coverage