[
] 171
volcano ballooning prior to eruption, landslides and
land subsidence.
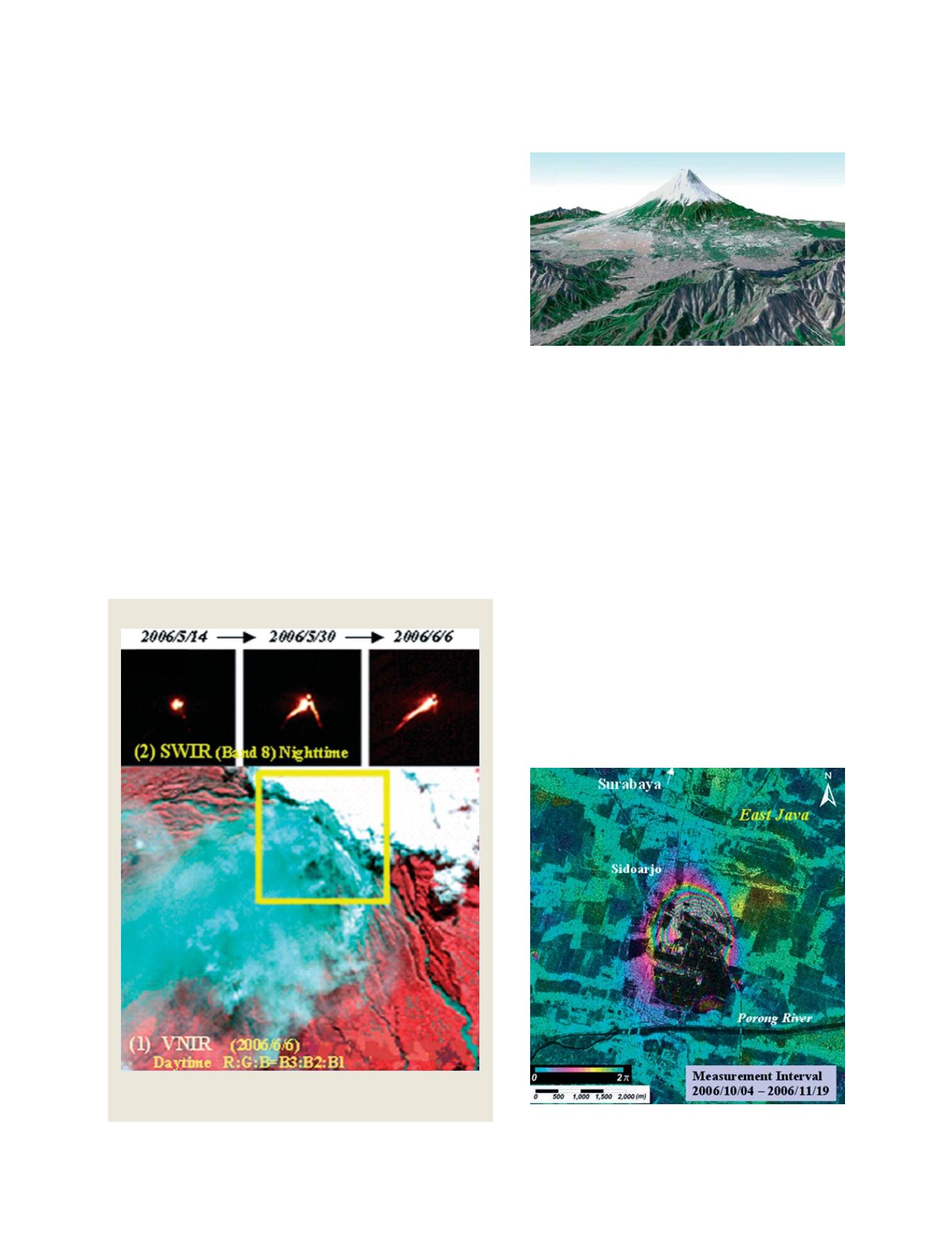
PALSAR was used to monitor land subsidence related
to exploration drilling for hydrocarbons at Sidoarjo, East
Java. The drilling triggered the development of a mud
volcano on 29 May, 2006. The PALSAR interferometric
data showed the level of ground subsidence during a 46-
day period from October to November 2006. The
interferometric fringes, which are colored cyan, magenta
and yellow, indicated the subsided area. There were
seven cycles of fringes with the maximum subsidence
calculated as approximately 90 centimetres. Areas of wet
mud are insensitive to interferometry analysis and thus
produce the black tones spatially associated with areas
of subsidence. Monitoring the Sidoarjo area using
PALSAR allowed for assessment of whether the land
subsidence was increasing or decreasing with time,
which helped the local administrative authorities to
manage the rehabilitation process.
ate a Global Digital Elevation Model (ASTER G-DEM), which will
comprise a seamless global mesh at 30x30m resolution that extends
up into high-latitudes to cover even the most inaccessible moun-
tainous regions.
ASTER G-DEM could be used to provide topographic information
on entire drainage basins, which in turn could be used to inform
water management, irrigation for agriculture and hydroelectric power
generation for industries, as well as flood control planning.
Topographical data could also be applied to infrastructure design,
including roads, railways and pipelines for oil, gas and water.
Specifically such data could be used to plan the best route or pass,
establish any necessity for tunnels or bridges and, in general, to esti-
mate the amount of work necessary to complete a project.
Furthermore, through contribution to Global Earth Observation
System of Systems, ASTER G-DEM is expected to make substantial
contributions to understanding the Earth and its processes, includ-
ing water resource management, ocean and marine monitoring,
agricultural land use and mineral and energy resources.
Application of PALSAR data
PALSAR is an L-band interferometric sensor suitable for detecting
the three-dimentional movements on a land surface. It is capable of
detecting changes of as little as ten centimetres between different
dates of image acquisition. This interferometric capability is useful
for monitoring subtle movements prior to earthquakes as well as
Three dimensional image of Mt. Fuji derived from ASTER VNIR
image and ASTER G-DEM
Photo: METI/NASA retain ownership of
ASTER data. Processed by ERSDAC
Interferogram derived from a pair of PALSAR data. The circular fringe
pattern corresponds to the area affected by land subsidence
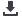
VNIR image captured the volcanic fumes and ash-fall damages. SWIR
images captured the overflow of hot lava
ASTER captured image of volcanic activity, Mt. Merapi, Central Java
Source: METI/NASA retain ownership of ASTER data. Processed by ERSDAC
Photo: METI/JAXA retain ownership of PALSAR data. Processed by ERSDAC
S
OCIETAL
B
ENEFIT
A
REAS
– D
ISASTERS