[
] 45
Europe, Africa and the Middle East. Links between
dust meningitis and large scale climate indexes, will
be explored as well. A work package on that subject,
coordinated by the Izaña-ARC in collaboration with
the BSC, CSIC and WMO, is presented within the
GEMS-MACC proposal to the EU-7FP.
Developing capacity-building activities
The Izaña-ARC manages a network of three multi-
channel, narrow-band radiometers (NILU-UV6) at the
permanent Argentinean bases of Ushuaia (55°S),
Marambio (64°S) and Belgrano (78°S); in Antarctica
since 1999, in cooperation with the Dirección
Nacional del Antártico (DNA/IAA Argentina), and the
Centro Austral de Investigaciones Científicas (CADIC,
Argentina). The selected stations are of scientific inter-
est for the monitoring and research of ozone, visible
and UV radiation in the region.
The three-station network is strategically designed
to obtain continuous ozone and UV transects from
inside to outside the polar vortex. Data is routinely
published in WMO Antarctic bulletins.
5
The Brewer
spectrophotometer from the Instituto Antártico
Uruguayo (IAU, Uruguay) installed at the Artigas
Antarctic base was fitted and calibrated at the Izaña-
ARC. Personnel from the IAU have also been trained
in ozone and UV observation techniques at the centre.
Within the WMO-GAW programme, the Izaña-ARC
maintains a ‘twinning’ partnership with the Ushuaia
OMI/AURA, with more than a dozen atmospheric components,
using advanced scientific instrumentation, has been performed at
Izaña. The FTIR will participate in the Total Carbon Column
Observing Network (TCCON). It focuses on the detection of total
amounts of greenhouse gases with a precision higher than 0.1 per
cent. New instruments and methodologies are being tested and
developed at Izaña, such as high-accuracy water vapour with GPS,
FTIR, photometric techniques and radiosondes, total column CO
2
with spectral sunphotometers, and new developments of Brewer
spectrophotometers for accurate measurements of aerosols and
other atmospheric compounds.
The Izaña-ARC has introduced to the air-quality field new
methodologies and instrumentation, which are normally used in
atmospheric research. Nano-particle counters and multi-angle
absorption photometers have been used in urban areas for a better
estimation of aerosols from vehicle exhaust emissions. The scien-
tific DOAS technique is used in Santa Cruz de Tenerife to quantify
reactive gases in two sectors of the city, in an operational way.
Improving the rate of implementation and capacity
A new proposal on the WMO Sand and Dust Storm (SDS)
Warning System (WS) was accepted at the Scientific Steering
Committee meeting for the SDS project (November 2006,
Shanghai, China). The main project objective is to establish a
WMO-coordinated global network of SDS forecasting centres that
deliver products useful for a wide range of users in reducing the
impact of SDS.
For Europe, Africa and the Middle East, Spain is currently creat-
ing a WMO regional centre for SDS. A partnership of three research
institutions comprises the regional centre: the INM, through the
Izaña-ARC, the Barcelona Supercomputing Centre (BSC), and the
Earth Sciences Institute ‘Jaume Almera’ (IJA-CSIC). This regional
centre will deal with both operational and scientific aspects related
to atmospheric dust monitoring and forecasting. The system is
primarily based on the Dust Regional Atmospheric Model
(DREAM), which provides daily dust forecasts for the above-
mentioned region;
4
the Meteosat Second Generation, from which
new space and temporary hi-res dust products can be obtained,
which are helpful for SDS monitoring; other satellite-based prod-
ucts, and the existing ground-based networks of lidars and
sunphotometers.
The first national UV Index (UVI) forecasting model in Spain
was developed by the Izaña-ARC. It covers the Iberian Peninsula,
the Balearic and Canary archipelagos and northern Africa.
Diffusion campaigns about the UVI and solar protection were
carried out in collaboration with dermatologists and pharmacists.
The first measurement programme for pollen and spore content
in the atmosphere was implemented in the Canary Islands by the
Izaña-ARC in 2004. Nowadays, it provides essential information
to allergologists. The Izaña-ARC also collaborates with epidemi-
ologists on studies focused on the relationship between PM10
(particles measuring 10μm or less) and mortality in the Canary
Islands.
However, the most ambitious programme related to health
focuses on meningitis epidemics over the Sahel. Certain environ-
mental factors, such as low absolute humidity, land cover types
and dusty atmospheric conditions, may play an important role in
meningitis. The relationship between dust intrusions over the
Sahel and meningitis epidemics will be studied by the SDS WS for
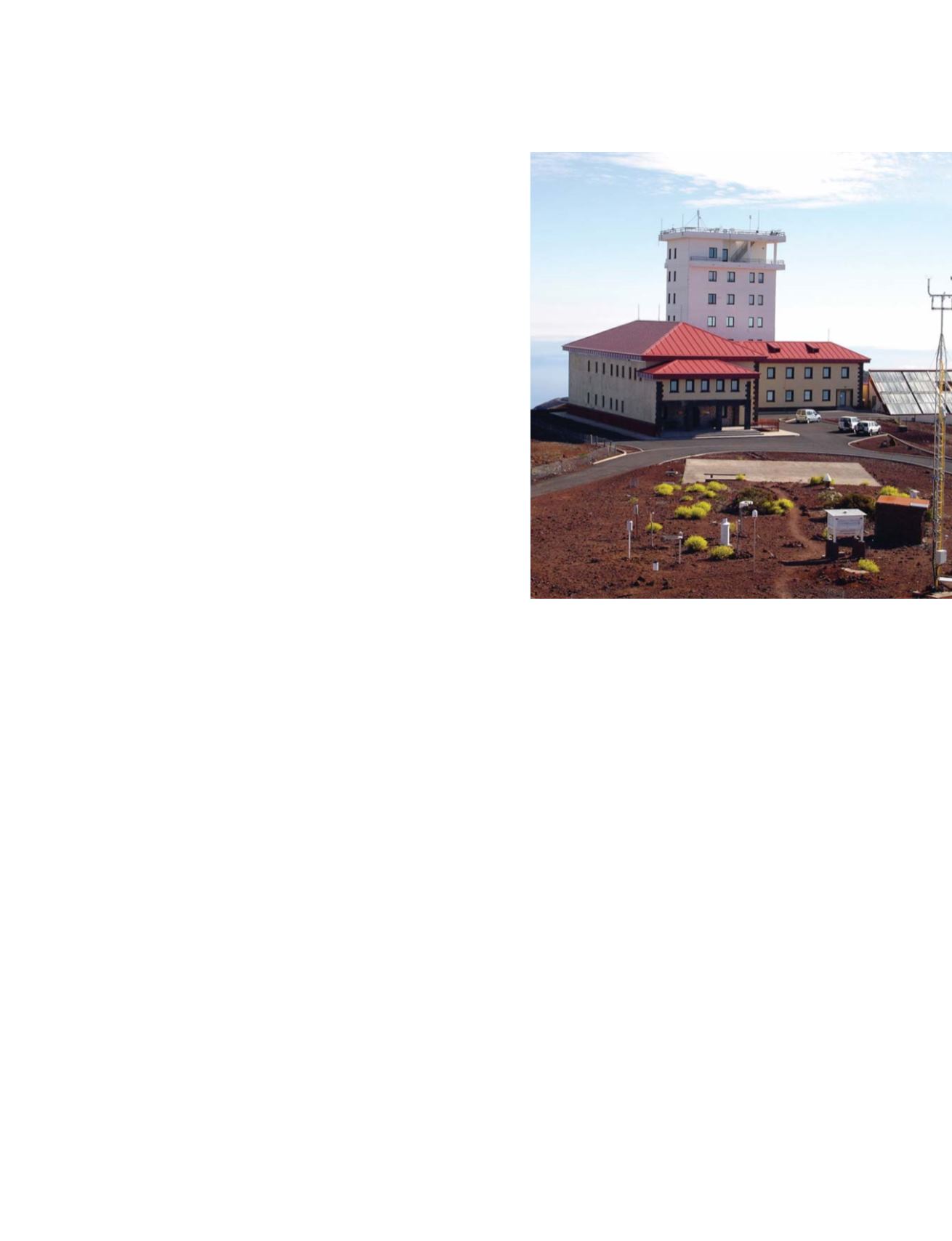
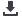
The high altitude Izaña super site
Photo: INM
N
ATIONAL
& R
EGIONAL
R
EPORTS