[
] 47
A
griculture
• The more targeted forecasts are provided by USQ’s
climate scientists and agronomists using peer
reviewed and verified climate forecast systems,
mostly developed in-house
• Aspects associated with gathering the exact needs
of growers and millers are derived from exhaustive
workshops held in every growing region of the
state. These workshops are highly effective and
facilitated by a well-recognized extension specialist,
who is also versed in climate forecasting systems
and their output.
Stakeholder involvement
Stakeholders were identified following extensive meet-
ings and workshops with the leading marketing and
export agency and the leading grower representative
body in the Queensland sugar industry. The following
stakeholders were consulted within a focused meeting
and workshop environment:
• QSL
• The Queensland Cane Growers’ Council and each of
its local branch offices
• Each of the eight sugar mill managers and key staff
• Some individual growers known to the project
managers though previous research project activity.
The focused meeting and workshop process distilled
the key issues, although this took a number of months
to achieve.
Key agencies including the UK Met Office (Hadley
Centre), the Centre for Australian Weather and Climate
Research, James Cook University (JCU) and USQ were
among the agencies consulted on the research and
‘product’ output process, with USQ leading the project.
Climate forecast information and associated research
is provided by climate scientists at USQ in collaboration
with the Bureau of Meteorology (Australia) and the UK
Met Office. Aspects related to ECMWF involvement are
negotiated through the UK Met Office.
Targeted output for the sugar industry is provided
by USQ’s Australian Centre for Sustainable Catchments
through the auspices of QSL specialist management
staff and local branch offices of the Queensland Cane
Growers’ Council and the Queensland Department
of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries. More specific
output will be provided through focused workshops
conducted directly with various agencies involved with
the sugar industry.
USQ (previously through the Queensland govern-
ment) has established its own published and verified
targeted seasonal climate forecasting system and this
forms the mainstay of the required detailed seasonal
climate forecasting outputs for the sugar industry.
Importantly, this system can be seamlessly integrated
into (sugar) crop simulation models such as APSIM and
other yield forecasting models.
2
With regard to the ‘new generation’ of climate model
outputs (GCM) to be incorporated in a research frame-
work for long-lead decision-making, agreements have
• Close attention is paid to the output of probabilistic forecasts
of likely extreme conditions, especially the potential for
excessive rainfall according to the user’s pre-defined criteria,
but also in terms of aspects such as forecasts of numbers of
frosts through the growing season and the need for extra
irrigation activity
Source: Y. Everingham and QSL, 2012
An example of climate forecasting-yield forecasting output from a
past year, using both targeted seasonal climate forecasting and
crop modelling for each of the terminal mill regions in Queensland
Source: After Hammer, 2000; Everingham et al., 2002; Stone and Meinke, 2005
The relationships between scale, information, content and
decision makers in defining a systems-based approach to
applying seasonal forecasts in agriculture – a key example
from the sugar industry
Seasonal forecasts and decision-making
Industry, Business and Resource Managers, Government
Scale Axis
Farm
General
Targeted
Harvest, Transport, Mill
Catchment Marketing
Policy
Information Axis
• Water
allocation
• Planning
and policy
associated
with
exceptional
events
• Crop size
forecast
• Early
season
supply
• Supply
patterns
Shipping
Global
supply
• Land and
water
resources
management
• Environment
management
• Improved planning
for wet weather
disruption - season
start and finish
• Crop size forecast
• CCS, fibre levels
• Civil works
schedule
• Irrigation
• Fertilization
• Fallow
practice
• Land prep
• Planting
• Weed
management
• Pest
management
General seasonal forecasts
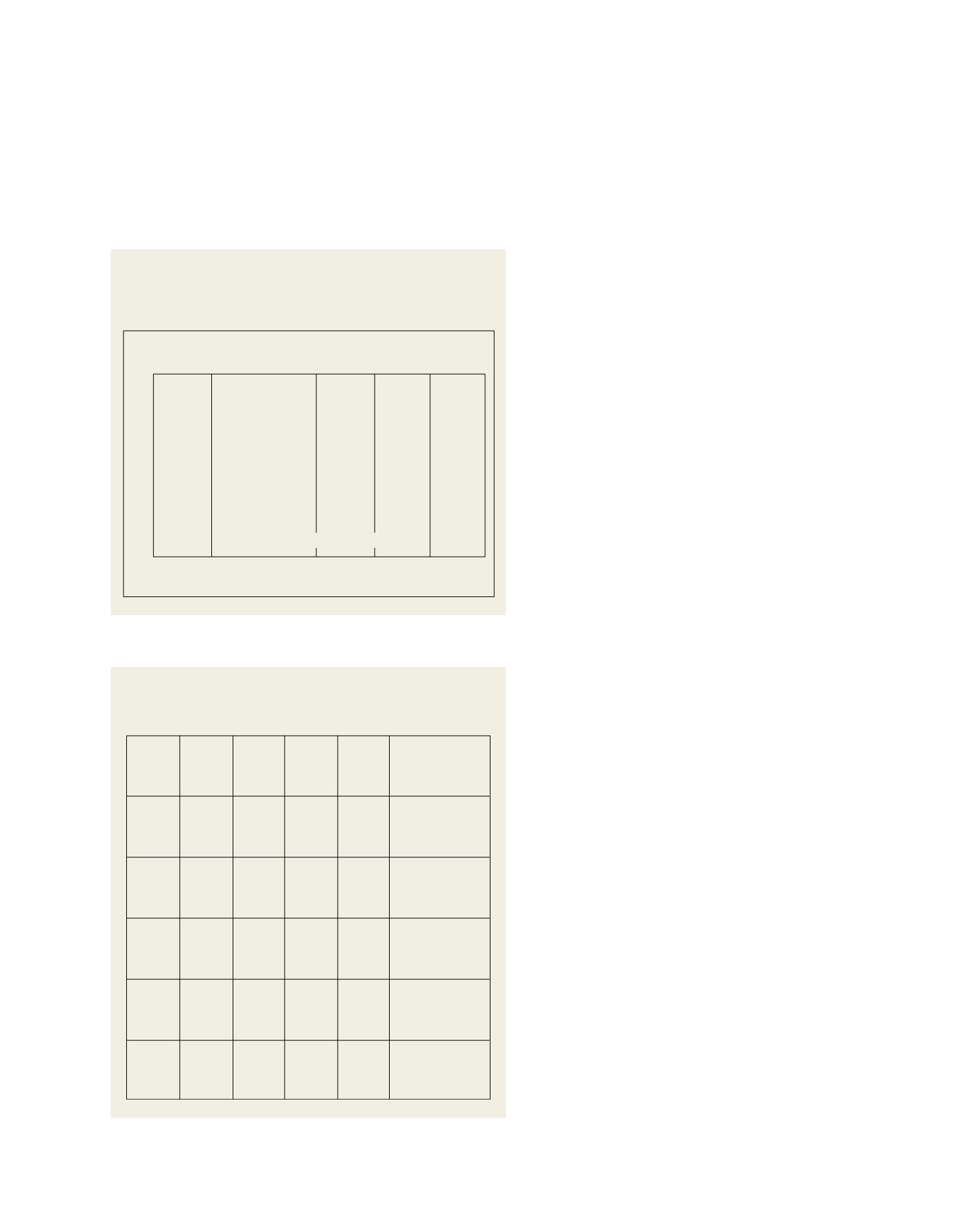
Terminal
Region
Forecast
(t/ha)
Standard
error
(t/ha)
Historical
Mean
(t/ha)
Simulated
Yield
Component
Comment
Sugar yield
forecast is
unchanged
from last month
Biomass
Biomass
Biomass
Biomass
Biomass
11.0
10.8
17.1
10.6
10.5
0.937
1.141
0.915
1.109
0.860
11.4
11.7
17.0
10.9
10.3
Bundaberg
Mackay
Townsville
Lucinda
Cairns/
Mourilyan
Sugar yield
forecast is
unchanged
from last month
Sugar yield forecast
is slightly down
(0.1 t/ha)
from last month
Sugar yield forecast
is slightly down
(0.2 t/ha)
from last month
Sugar yield forecast
is slightly down
(0.2 t/ha)
from last month