[
] 262
A
dAptAtion
And
M
itigAtion
S
trAtegieS
tion, governments and various customers are convinced of their
value. This is only helping to ensure adequate financial resources
are allocated to NHMSs in the future. The situation in many WMO
member countries, on the other hand, is quite the opposite. With
NHMSs and weather products in such countries being of a gener-
ally low quality and quantity, governments are not seeing the
value of allocating additional resources to them. This is having
a negative impact on the economy and human safety in affected
countries and serves as an obstacle for development, contradict-
ing many initiatives that have been set up to reverse this. The
functions of NHMSs, for example, are closely related to five out of
eight Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). These goals tackle
poverty and hunger, health, education, environment and develop-
ment partnerships.
International collaboration and development
projects in essential role in strengthening the
national capabilities
Both natural disaster early warning systems and climate
change adaptation plans offer good perspectives for devel-
opment cooperation. The expertise of developed country
NHMSs and atmospheric research organizations may
be used in assisting developing countries and those in
economic transition. According to WMO, several coun-
tries – including Japan, Korea, China, Australia, Finland,
the UK, Spain, France, Germany and the US – are actively
assisting developing countries.
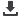
Finland and the Finnish Meteorological Institute
(FMI), for example, have supported more than 80 coun-
tries since the 1980s. At the moment, projects related to
adaptation to climate change and natural disaster early
warning systems are being run in small island devel-
oping states, both in the Caribbean and in the Pacific,
the Southern African Development Community coun-
tries, Peru, Nepal and Vietnam. The core of current
programmes involve institutional cooperation between
both FMI and NHMSs in other countries. FMI is also
working alongside China, India, Russia, Argentina and
Brazil besides several European and North American
countries in scientific projects.
Investments in natural disaster early warning systems
and preparation of climate change adaptation strategies are
good investments. Besides bi-lateral activities these fields
offer good opportunities for new programmes, especially
under major development donor organization frameworks
such as those of the World Bank, regional development
banks or the European Commission.
Consultancy and development cooperation projects since the 1980s
Scientific collaboration (blue); consultancy/development cooperation (red)
Source: FMI presentation material, 2009
Source: VTT Technical Research Centre Publications 665, 2007
Road transport
Pedestrians
Railway transport
Maritime
Aviation
Logistics
Building construction and facilities management
Agriculture
Expected total benefit with current services
13–18
80–100
0.4
32–50
54–55
Tens of millions
15–30
34
> 239–303
A summary of the socioeconomic value of the FMI for different user
segments. In 2007 the FMI budget was about EUR50 million