[
] 27
Chinese space-based Earth observation
system – a contribution to GEOSS
China Meteorological Administration
T
he 21st century is a new age that will see a global boom
in Earth observation science. In recent years, there has
been great progress in space-based Earth observation
systems in China. Chinese satellites, including the FengYun mete-
orological satellite series, Resource satellite series, Ocean
satellite series and Environmental and Disaster Reduction satel-
lite series, have developed and continue to do so. With all these
satellite series in place, a Chinese integrated Earth observation
system, enhancing the scope and levels of Earth observation,
will come into being. Based on this primary established Chinese
Earth observation system, China has taken full advantage of
these satellites in weather, disaster monitoring, and resource
and environment management.
Meteorological satellite
China began to develop its meteorological satellite independently in
the early 1970s. The first polar orbiting experimental meteorologi-
cal satellite (FY-1A) was launched successfully in the late 1980s. So
far, a total of eight meteorological satellites have been successively
launched, including four polar orbiting satellites and four geosta-
tionary satellites. As a result, two major series (the polar-orbiting
and geostationary series) of meteorological satellite systems have
taken shape – a network of two geostationary satellites has been
created to observe, and the orbiting satellites are backed
up operationally. In order to satisfy the increasing
demands of economy and society, China plans to launch
its second-generation polar orbiting meteorological
satellite (FY-3A) in 2008. This will carry 11 payloads,
and will be able to make all-weather global Earth obser-
vations with high spatial resolution.
Since the early 1980s, meteorological satellite data has
been applied gradually to weather forecasting/predic-
tion and ecological environment monitoring, among
other things. With the constant deepening of applica-
tion research on satellite meteorology and continuous
optimization of satellite remote-sensing products, the
polar orbiting and geostationary meteorological satel-
lite data have been applied widely to many fields such
as weather forecasting, climate prediction, natural disas-
ter monitoring, crop production estimation,
environmental monitoring and space weather. Important
remote sensing information arising from meteorologi-
cal satellites has been provided to governments and
relevant departments for their decision-making, thus
playing a vital role in many fields such as disaster
prevention and reduction, and economic development.
Resource satellite
The China-Brazil Earth Resource Satellite (CBERS) was
jointly financed by China and Brazil. The CBERS project
was set up in 1986, and the protocol on research and
production of the Earth resource satellite was signed by
both governments in 1988. According to the protocol,
CBERS is based on a Chinese concept, with 70 per cent
of overall funds financed by China and 30 per cent by
Brazil. China is responsible for the satellite system
concept; the development of the thermal control subsys-
tem, attitude and orbit control subsystem; the ultra short
wave tracking, telemetry and command system (TT&C);
onboard data management; onboard overall electro
circuit; charge-coupled device (CCD) camera; infrared
multi-spectrum scanner; CCD data transmission; onboard
digital high-density magnetic recorder; infrared data trans-
mission; the space environment monitoring system and
the integration, electronic test and large-scale test of the
first CBERS. Brazil is responsible for the development of
the structural subsystem, power subsystem, S-band
TT&C, data collection subsystem, and development of
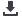
Global multi-orbit mosaic image
This image is made from FY-1C multi-orbit data on 9 August 2000. It shows
how the satellite scans and circles around the Earth. As the influence of the
solar zenith angle is not corrected, the edges where orbits meet are obvious.
Global image mosaic is the basic form for global environment monitoring and
data application
National Satellite Meteorological Center, China Meteorological Administration
N
ATIONAL
& R
EGIONAL
R
EPORTS