[
] 29
The main use of HY satellite is to detect the marine environmen-
tal parameters of the China Seas, including chlorophyll
concentration, suspended sediment concentration, dissolved organic
matter and pollutants, as well as sea surface temperature. The satel-
lite will play an important role in developing and utilizing the marine
bio-resources, constructing and managing the harbour, detecting
ocean pollution, investigating and developing coastal resources and
studying global environmental changes.
Other satellites
A small satellite called Beijing No. 1, created with the cooperation of
Beijing Land-view Mapping Information Technology Co., Ltd. and
Surrey Satellite Technology Co., Ltd., was launched on 27 October
2005. Its sensor measures four metres, and it is considered to have
the highest resolution among all the transmission-type micro-satel-
lites made in China. The satellite can send 32-metre long spectrums
and cover an area of 600 kilometres. It has the greatest width among
the same type of satellites produced in the world. The satellite can
work in space for at least five years.
In the coming few years, China will create an environment and
disaster monitoring satellite constellation by deploying a number of
optic and synthetic aperture mini-satellites in space. The satellite
constellation will become the world’s first space-earth based inte-
grated disaster management system, taking advantage of both ground
disaster information systems and space resources. The constellation
will be constructed in two phases. Phase I was completed between
2005 and 2006, during which two optic mini-satellites and one
synthetic aperture mini-satellite were deployed. The 2+1 deployment
pattern will produce a 48-hour satellite return visit capacity to meet
partial disasters alleviation needs. The Phase II project is scheduled
to become operational in 2010. By that time the 4+4 deployment
pattern (four optic mini-satellites and four synthetic aperture mini-
satellites) will make a 12-hour return visit possible.
China Integrated Earth Observation System; a 10-year plan
In response to the international GEOSS 10-Year Implementation
Plan, China is now organizing the experts of different ministries and
commissions to schedule the China Earth Observation 10-Year Plan,
which will be made up of one collectivity section and five important
observation system plans: the China climate observation system plan;
the China atmosphere chemistry observation system plan; the China
ocean observation system plan; the China hydro cycle observation
research plan, and the China carbon cycle observation research plan.
Meanwhile, the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology has
added the ‘Earth Observation and Navigation Techniques’ research field
to the National High Technique Research and
Development Program, and expects to establish an inte-
grated research and development system for Chinese Earth
observation and navigation technology.
International cooperation
China encourages bilateral and multilateral international
and regional cooperation in space programmes. Since
1985, China has signed a series of intergovernmental
and interdepartmental agreements, protocols and memo-
randums on space science and technology and its
application in foreign countries, and has established a
long-term cooperative relationship with these countries.
The Galileo project is the largest cooperation project in
science and technology between China and EU so far.
China and the European Space Agency (ESA) successfully
launched TC-1 and TC-2 and implemented the Geo-space
Double Star Exploration Project, managed by China and
ESA. In 1997, the Chinese Ministry of Science and
Technology and ESA began long-term cooperation on
projects such as the applications of ERS-1/2 satellite data
and the Dragon Project in 2003 for the application of
ENVISAT data in the field of agriculture, forestry, envi-
ronment and city planning. They also began working
together on exchanges and training in aerospace field.
China, is working in close cooperation with EUMET-
SAT, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric
Administration (NOAA), the World Meteorological
Organizatoin (WMO) and many prospective data
provider partners to develop GEONETCast, a global
network of satellite-based data dissemination systems
providing environmental data to a worldwide user
community. China attaches great importance to the Asia-
Pacific
region.
The
China
Meteorological
Administration, on behalf of the Chinese Government,
donated six sets of FENGYUNCast user receiving
stations to Bangladesh, Indonesia, Iran, Mongolia,
Pakistan and Thailand in 2006. In October 2007,
another 11 sets of FENGYUNCast user receiving stations
were donated to the Democratic People’s Republic of
Korea, Kyrghyz, the Lao People’s Democratic Republic,
Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, the Philippines, Sri Lanka,
Tajikistan, Uzbekistan and Vietnam. At present, 17
countries in the Asia-Pacific region are able to receive
Earth observation data through the FENGYUNCast. In
this regard, a positive impact has been made in initia-
tives for disaster prevention and reduction, economic
and social development and promoting the implemen-
tation of GEOSS in the region.
Building the GEOSS is an inexorable trend whether
due to the demands of society or the development of
science and technology. This will establish long-term
and stable Earth observation satellite systems and coor-
dinated national satellite remote sensing application
systems, which are especially designed for specific
departmental operations. China will continuously
promote the establishment of the GEOSS, working to
realize stereo viewing and dynamic monitoring on land,
atmosphere and ocean the world over.
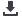
China Meteorological Administration, donation of FENGYUNCast
user stations
N
ATIONAL
& R
EGIONAL
R
EPORTS