[
] 191
T
HE
21
ST CENTURY
has seen the emergence of e-Science as
a new research environment.
2
In the past few years, many
e-Science related programmes and projects have been
launched worldwide. The Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS),
the top research organization in China, has also been carrying
out many initiatives in e-Science since 2002.
3
What is e-Science?
A new word rich with meanings, e-Science represents a new style
of doing research in the Information Society, with the great advan-
tage of information and communication technologies (ICT). John
Taylor, Director General of Research Councils in the UK, described
e-Science as follows: “e-Science is about global collaboration in
key areas of science, and the next generation of infrastructure that
will enable it; e-Science will change the dynamic of the way
science is undertaken.” While more and more countries pay atten-
tion to e-Science and take actions concerning it, there are quite
a few definitions and statements about what e-Science means. It
does not matter which explanation is better than others – a
common understanding should be that research is the objective
and new technologies are the methods of achieving it.
CAS is the top research organization of China, carrying out all
kinds of research in the natural sciences. CAS has more than
100 institutes and about 37,000 researchers. It has made a great
contribution to the country and intends to go on playing a
leading role in the national development of science and tech-
nology. Since the end of the 20th century, the advancement and
applications of ICT has vastly changed people’s lives, as well as
researchers’ work. To make sure those scientists have a sound
research environment with an advanced information infrastruc-
ture, CAS has invested a lot of resources and efforts in
informatization construction over the past five years. Along with
this progress, e-Science became an objective and an important
task of the CAS Informatization Programme 2001-2005.
Currently, the next five-year programme for 2006-2010 is being
devised. e-Science has been chosen as the main direction in the
new programme.
CAS Informatization Programme 2001-2005
The main object of the CAS Informatization Programme 2001-
2005 was to significantly improve the CAS information
infrastructure, based on finding a common platform and services
on which all institutes and researchers of CAS could run.
4
Some
key projects of the programme are the upgrade of the CAS
network, the construction of a supercomputing environment, the
scientific database and its applications, and a video conferencing
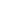
system, among others. Table one shows the main achievements
of the programme.
CAS e-Science Initiative 2006-2010
In 2004, CAS started planning the new programme for CAS
Informatization Construction under the national 11th five-year
programme 2006-2010. At almost the same time, the Chinese
Government organized more than 1,000 experts to fulfil a middle
and long term national plan untiil 2020 for the development of
science and technology. Some experts had worked for both plans.
CAS tried its best to follow and match the national plan to its
own scheme for the next five years.
5
The ultimate goal, or the vision, of CAS Informatization is to
build a digital CAS, which would be an ideal form of the academy
to take in the Information Society. There are two major missions:
one is e-Science and the other is Academia Resource Planning
(ARP). ARP is a new concept borrowing from Enterprise Resource
Planning (ERP). e-Science means scientific research activities in
an informatized environment; ARP means administration for
scientific research in an informatized environment.
CAS e-Science and Virtual Lab
Baoping Yan, Kai Nan, Chinese Academy of Sciences
1
Infrastructure
Item
By 2000
By August 2005
Core Bandwidth
1Gbps
2.5Gbps
CAS Network
Backbone Bandwidth
2Mbps
N x155Mbps +2.5Gbps
International Links
55Mbps
620Mbps + 12Gbps
Peak Perfomance
130GFLOPS
5.5TFLOPS
Super computing
Storage
2.1TB
182TB
Linpack
50GFLOPS
4.2TFLOPS
Member Institutes
21
45
Scientific Database
Number of databases
180
388+
Data Volume
725GB
13TB
Table 1: Progress on information infrastructure