Natural language
– Programming computers to understand
natural human languages
Neural networks
– Systems that simulate intelligence by attempt-
ing to reproduce the types of physical connections that occur in
animal brains
Robotics
– Programming computers to see and hear and react to
other sensory stimuli
Games playing
– Programming computers to play games such as
chess and checkers
AI has two objectives:
• To study the mechanisms of intelligence
• To build programs able to respond to intelligent activities.
History of artificial intelligence
In 1956 John MacCarthy, regarded as the father of AI, organized
a conference to draw the talent and expertise of others interested
in machine intelligence for a month of brainstorming. He invited
them for “the Dartmouth summer research project on artificial
intelligence.” From that point on, because of MacCarthy, the field
would be known as Artificial intelligence. The Dartmouth confer-
ence did bring together the founders in AI, and served to lay the
groundwork for the future of AI research. For that purpose, he
joined Minsky, Newell, Simon and Shannon.
The 1970s and the beginning of the 1980s were marked by the
realization of many expert systems. The seventies were also the
years of the first experiments with mobile robots (for example,
Shakey the Robot of the SRI at Menlo Park, California). AI first
developed in USA, before interesting researchers in Europe and
Asia in the mid s1970s.
Different models of artificial intelligence
Today, three big models are used by researchers and engineers in
artificial intelligence:
• Symbolic models (Symbolic AI)
• Neuromimetic symbols (Connectionist AI)
• Statistics models (AI Statistics).
Fields of artificial intelligence
Robotics
– Robotics is the field of computer science and engineering
concerned with creating robots, devices that can move and react to
sensory input. Robotics is one branch of artificial intelligence. Robots
are now widely used in factories to perform high-precision jobs. They
are also used in special situations that would be dangerous for
humans – for example, in cleaning toxic wastes or defusing bombs.
Although great advances have been made in the field of robotics
during the last decade, robots are still not very useful in everyday life.
Aware of the numerous challenges arising from robotics (cost
and heavy weight), the scientists of IMSI (Institute of Materials
and Intelligent Systems) are trying to find more practical and
affordable ways.
Learning
– The domain of learning in AI is merely an attempt to
simulate with a machine the remarkable aptitude that man has
to learn. Hence the importance of theoretical researches which
try to provide a formal environment to machine-based learning.
Speech Recognition
– Many psychological studies based on the
child’s simultaneous development of language and intelligence
and on the comparison between man and the chimpanzee
revealed the importance of language in the development of intel-
ligence. In speech recognition, we can distinguish two methods:
• The systems of speech recognition which have the objective of
decoding the pronounced sentence word by word
• The systems of speech understanding which have the objective
of understanding the pronounced sentence.
Understanding natural languages
– Progress on building computer
systems that process natural language in any meaningful sense
requires considering language as part of a larger communicative
situation. Natural-language processing offers the greatest potential
rewards because it would allow people to interact with computers
without needing any specialized knowledge. You could simply walk
up to a computer and talk to it. In fact, two essential dimensions
are significant: understanding texts and automatic translation.
There are also voice recognition systems that can convert
spoken sounds into written words.
[
] 196
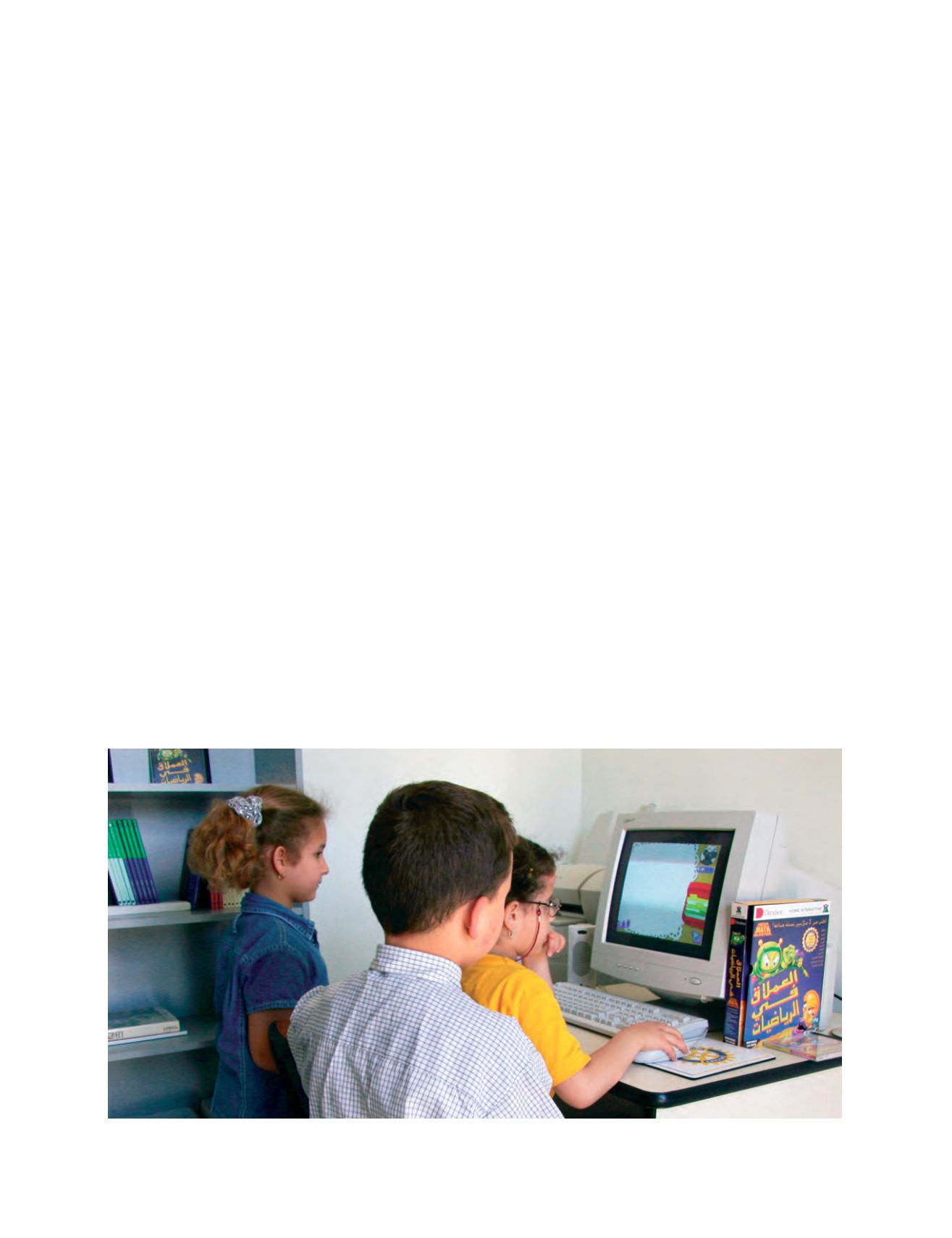
Kindergarten children using computers to learn